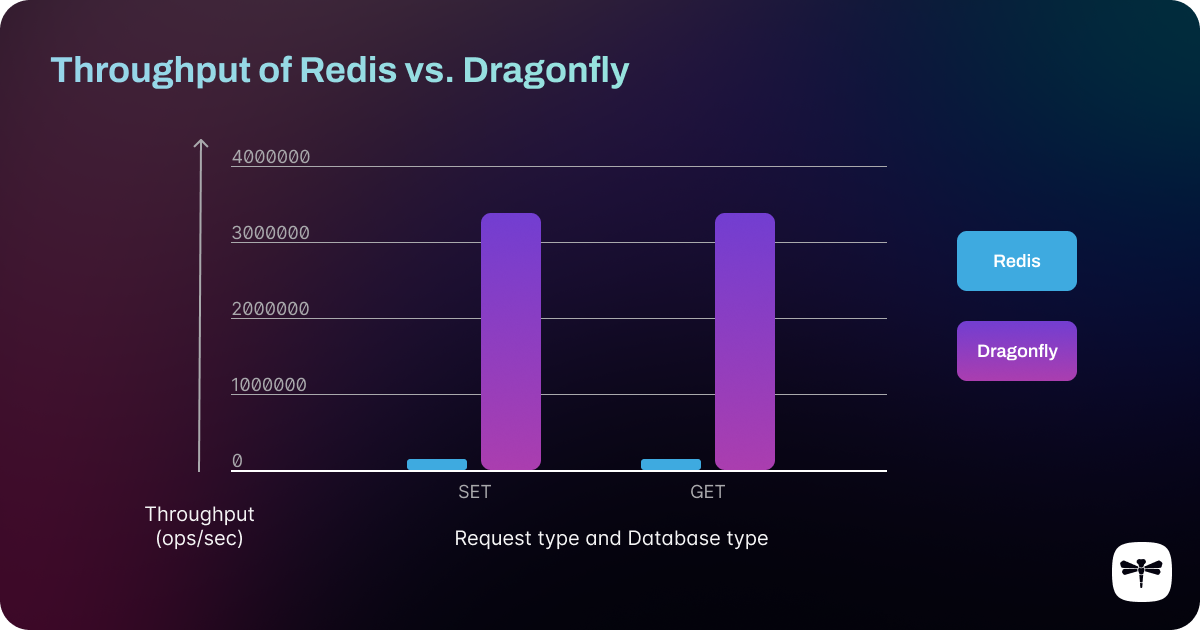
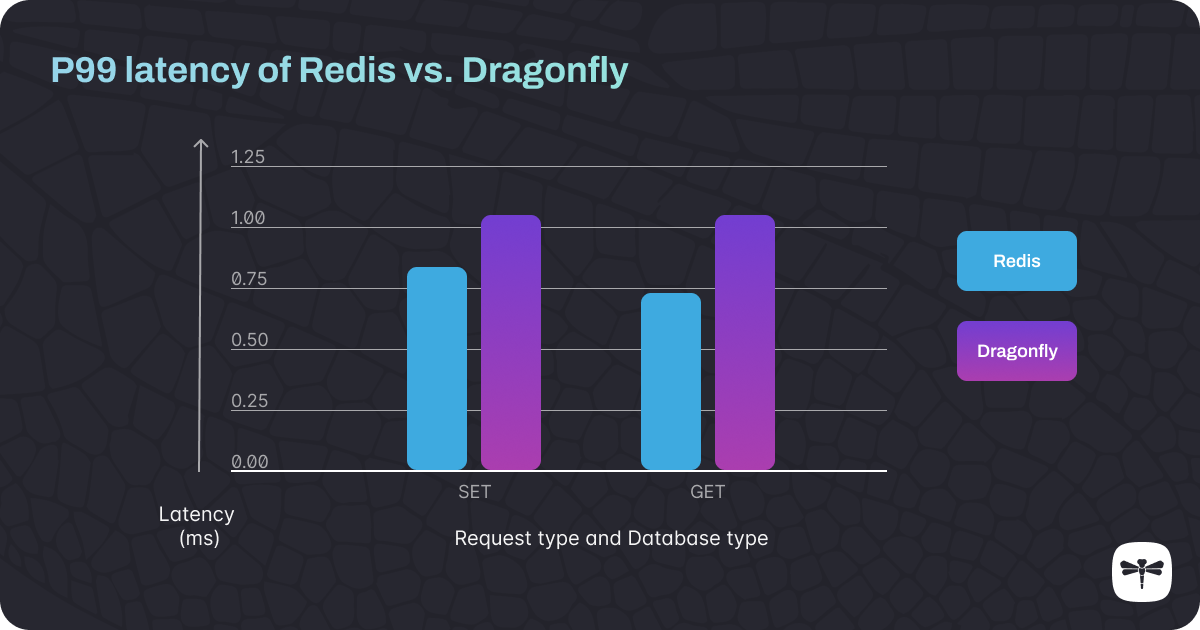
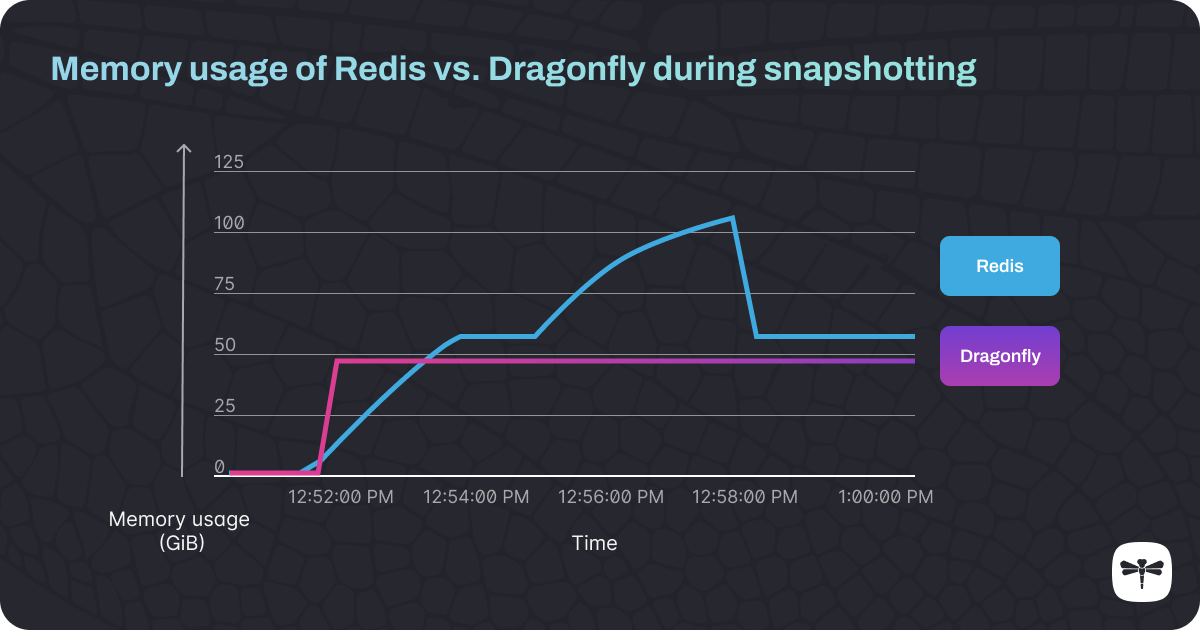
Domesticate dragonfly for Snapp ODE. Setting up dragonfly with Docker, deploy on Kubernetes with a single Pod, deploy using Charts. Testing dragonfly with a simple load testing application.
Dragonfly is a drop-in Redis replacement that scales vertically to support millions of
operations per second and terabyte sized workloads, all on a single instance.
Dragonfly gives you so much more with a complete, modern engine architecture that’s fully
compatible with the Redis and Memcached APIs.
docker pull docker.dragonflydb.io/dragonflydb/dragonflydocker run --ulimit memlock=-1 -p 6379:6379 docker.dragonflydb.io/dragonflydb/dragonflyNow you can use redis sdk to connect to dragonfly cluster.
rdb := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Addr: "localhost:6379",
Password: "", // no password set
DB: 0, // use default DB
})
err := rdb.Set(ctx, "key", "value", 0).Err()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
val, err := rdb.Get(ctx, "key").Result()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println("key", val)Dragonfly also provides helm charts in order to deploy an instance on kubernetes.
helm install dragonfly charts