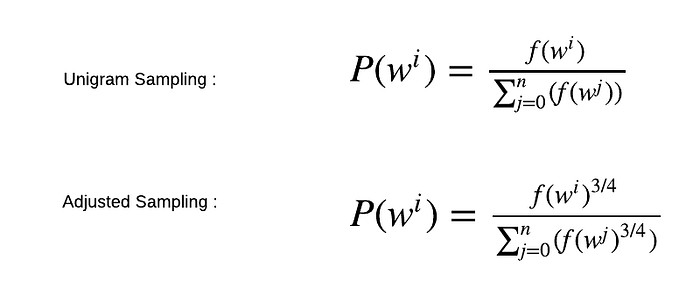Main concepts of NLP and how to implement them. Take note that this is a review on NLP and takes inspiration from Stanfords CS224 by Professor Christopher Manning.
- BERT-for-Sentiment-Analysis_PromisedNeverland.ipynb is a modified version of Chris Tran's "Fine Tuning BERT for Sentiment Analysis" using my own data. Take a look at his portfolio at https://chriskhanhtran.github.io/about/!
- Language has several layers to analyze, and thus is highly complex.(언어는 다양한 단계및 측면에서 분석하여야 하기 때문에, 상당히 복잡한 영역이다)
- phonetics(음성론):언어자체가 어떻게 들리는지에 초점을 맞춤
- phonology(음운론):언어가 소리를 배합하는 체계에 초점을 맞춤
- morphology(형태론):단어의 구조에 초점을 맞춤
- syntax(통사론):문법 구조에 초점을 맞춤
- semantics(의미론):문장 및 표현의 표면적 의미에 초점을 맞춤
- pragmatics(화용론):문장 및 표현의 맥락에 따른 의미에 초점을 맞춤.(ex.A:(시간약속 늦은 친구에게)너 지금 몇시인지 알아? B:미안미안, 다음부터 안 늦을게!)
In order to fully grasp the concept of language one must be aware of all these levels of language, which is exactly why NLP is a difficult field in computer sciences. The main problem is: how do you get a computer to understand these highly complex layers of language?(언어를 제대로 이해하기 위해서는, 언어의 모든단계를 이해해야 할 필요가 있다. 하지만, 문제가 하나 발생한다: 어떻게 컴퓨터한테 이 모든 단계를 이해하게 만들지?) Not only that, every language has its own set of unique rules. How can a computer learn these specific rules? These are some of the main tasks that the NLP field must tackle.(뿐만 아니라 모든 언어마다 각자 고유의 규칙이 있다. 어떻게 하면 컴퓨터가 이런 구체적인 규칙들을 배울 수 있는 것일까? 자연어처리 영역에서 이런 문제들을 주로 다루고 있다.)
First things first, how do we make a computer understand words? To be more specific, how does a computer see representations of words? This whole process is something called encoding.(우선 우리가 생각해야 할 것은, 컴퓨터가 어떻게 단어를 이해하는 것인가이다. 좀더 구체적으로 말하면, 컴퓨터는 인간의 단어를 어떻게 인식하는 것일까? 이런 과정을 바로 인코딩 이라 말한다)
The following methods and models have different approaches of encoding. They are listed in this order as the models progress and improve they are built up on the previous models and attempt to modify any flaws that the previous models may have had.(다음 모델들은 각자 다른 방식으로 인코딩을 하게 된다. 자연어처리의 모델들은 순서가 중요한데, 그 이유는 지난 모델들이 안고있는 문제점들을 개선해나가는 과정에서 모델들이 발전해오기 떄문이다.)
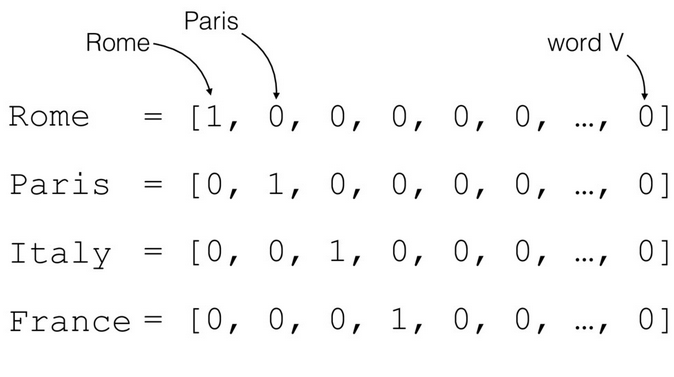
- Considered one of the most basic forms of encoding(인코딩의 기본형으로 간주됨)
- Any repeated words in a corpus are eliminated, thus making each unique word appear once. Note that words with different forms are considered different words. For example 'cats' and 'cat' are considered different words.(단어들의 집합에서 중복되는 단어들을 제외하여, 고유의 단어 하나만 남긴다. 한가지 주의 할것은, 완전히 똑같은 형태의 단어가 아니면 다른 단어로 처리된다는 것이다. 예를 들면 'cat'와 복수형의 'cats'은 다른 단어로 취급한다.
- Each unique word is given a specific index. To represent a specific word, that word's index is represented with a 1, while the rest are represented as 0.(각 고유의 단어마다 인덱스가 배정이 된다. 특정 단어를 표현하기 위해, 해당되는 단어의 인덱스는 1로, 나머지는 0으로 표현이 된다.)
This method is highly simplistic and easy to understand. However this method poses many flaws as well.(원핫인코딩은 상당히 단순하고 이해하기 쉬운 개념이다. 그러나, 많은 한계를 지니고 있다.)
- The size of a one-hot vector is dependent on the absolute size of the corpus. The larger the size of the text is, the larger the encoded vector becomes. The size of the vector will inevitably cause computing problems when it comes to speed.(원핫벡터의 크기는 코퍼스 크기에 절대적으로 의존한다. 텍스트양이 많아지면 많아질수록, 인코딩된 벡터의 크기 또한 늘어난다. 이는 결론적으로 연산의 속도가 느려지는데 크게 기여하게 된다.)
- One-Hot embeddings have another flaw in which they are not able to capture nuances between words as they are only comprised of 1's and 0's. To elaborate, a 'cat' and a 'tiger' can be considered as having many similarities. They both are felines, they have whiskers, etc. Yet, when your vectors look like this:
cat = [0,0,1,0]
tiger = [0,1,0,0]
it is very difficult to tell what similarities or differences these embeddings have.(원핫코딩의 치명적인 단점은, 1과 0만으로 구성되어 있기 때문에 단어간의 공통점, 차이점을 표현하기 매우 어렵다는 것이다. '고양이'와 '호랑이'는 생각해보면 고양이족인데다 생긴 것 또한 닮은 것들이 많아, 이런 단어간 유사함이 존재함에도, 단어의 인덱스에만 의존하여 벡터를 만들었기 떄문에 이런 내포되어 있는 정보를 표현하기 힘들다.)
- One-hot encoding itself may not be able to capture the meaning and contextual usage of words, but it is the foundation for vector representation of words, or to elaborate, Word2Vec.
- Bag of Words(BoW): While SLM's take into consideration the sequence of words preceding a target word(thus the order of the words are very important), the BoW encoding method only takes into consideration the frequency of words in a corpus. Similar to One-hot encoding, each word is assigned an index and the frequency of each word is assigned to that index.(BoW와 같은 경우 통계적기반 모델과는 조금 다르게, 단어들이 나열된 순서를 고려하는 것이 아니라 온전히 단어들이 출현하는 빈도를 바탕으로 인코딩하는 기법이다. 원핫 인코딩과 유사하게, 각각 단어마다 인덱스를 부여하여 단어가 출현하는 빈도수를 그 인덱스에 반영이 되는 인코딩 기법이다.
Like One-hot encoding, these count based methods of encoding cannot fully grasp the true meanings in a text. These count based methods are used to check the relevant importance of certain words or phrases. Using methods like cosine similartiy or TF-IDF, these count based methods can be used to check the similarity of two or more texts or to check the importance of certain words or phrases.(원핫인코딩과 비슷하게, 이런 카운트 기반의 모델이나 인코딩 기법들은 텍스트 내의 단어들의 의미를 완전히 담아내기에는 역부족이다. 하지만 이런 기법들은 문서간의 유사도 혹은 문서 내의 단어의 중요도를 파악하는데에 용이한 점이 있다.)
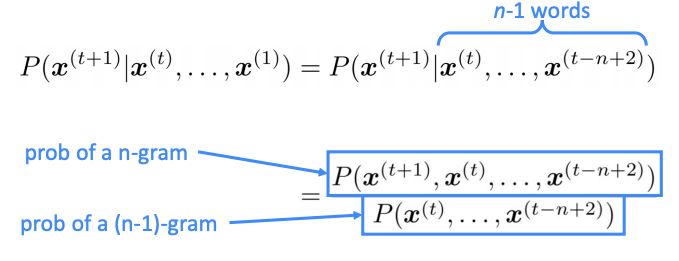
- SLM: Models use conditional probability, mainly the words used before a target word.(통계적 언어모델들은 흔히 지정한 단어 이전에 오는 단어들바탕으로 조건부 확률을 활용하여 그 단어가 나올 확률을 측정한다.)
- N-Grams: A variation of SLM. Instead of taking into consideration all the words that proceed a target word, it takes into account N-number of words. If it only takes into consideration of 1 word, it's considered a unigram, 2 words, a bigram, 3 words, a trigram and so on.(통계적 언어모델의 부류로, 지정단어를 선행하는 모든 단어들을 고려하지 않고, 선행하는 n개의 단어만 고려하게 된다. 몇개의 단어를 볼 것인지에 따라 unigram(1개), bigram(2개), trigram(3개) 등의 이름을 가지게 된다)
While in theory this seems like a reasonable approach to understanding language, there exists its limitations. In order to understand the statistical probability of a certain word or phrase, that word or phrase must appear a significant amount of times. This means that an enormous amount of text is needed to analyze the distribution of these words. There is also a chance that a certain word or phrase may not appear frequently enough. This problem is known as the sparsity problem.(이런 통계적 모델들의 한계점은 특정 단어의 사용확률을 측정하기 위해서 학습되어야 할 텍스트 양이 방대해야 한다는 것이다. 그렇게 함에도 불구하고 모든 표현들의 확률적 사용법이 완전히 학습될 것이라는 보장 또한 없다. 이렇듯, 충분한 양의 데이터가 없어 특정 단어들의 배열 규칙을 학습하지 못하는 경우를 희소(sparsity problem)이라고 한다.)
- Word2Vec: Traditional SLM's mainly focus on the words that precede a target words and make decisions based upon the frequency of words and phrases. Word2Vec's main approach is to use the context of the words to turn these words into vectors. Using a Neural Network Language Model(NNLM), the model will slide through the whole corpus that has been embedded as one-hot vectors. Using a designated amount of words around a target words through means of backpropogation, the model adjusts the embeddings from simple one-hot vectors to a vector comprised of nuanced floats that take a place within a vector space. These embedded vectors now have association with one another as the closer vectors are, the more similar they are in terms of context.
There are two main approaches to the Word2Vec representation. CBOW(Continuos Bag of Words) and Skip-Gram
- CBOW: Uses surrounding words to predict target word. Faster to train, works better for frequent words.
- Skip-Gram: Uses target word to predict the surrounding words. Comparitively more accurate, can be used on smaller dataset.
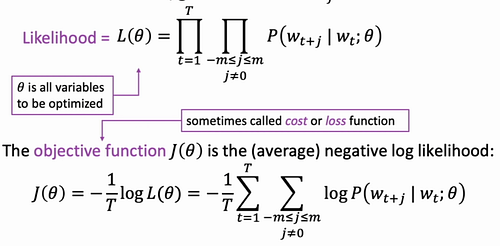
The main way Word2Vec optimized is by minimizing the following objective function.
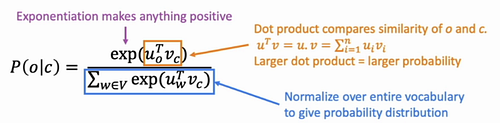
The finaly predictions are made upon passing the context words along with the target words into a softmax function and comparing the results to the actual one-hot encoding.
While this way of encoding words into vector representations is a huge step forward, there still exists problems: This model still takes up a lot of computing power. This is mainly caused by the way this model is trained. Since this model makes a vector representation by going through every word in this dataset, training takes up a long time.
So the Word2Vec method incorporates two methods to speed up the training process. Negative sampling and Heirarchical Soft-Max.
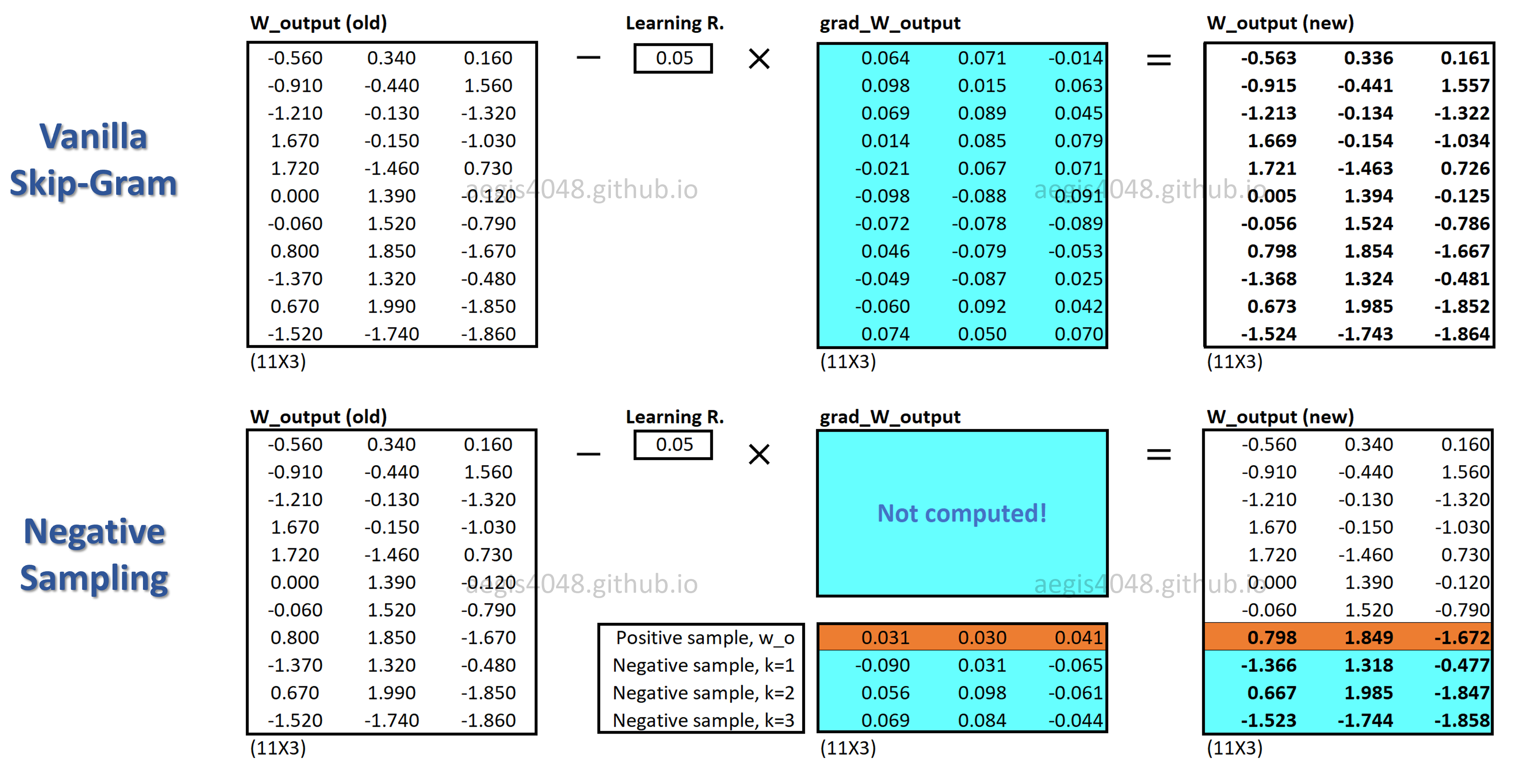
- Negative Sampling: Ideally, when training a neural model, all of the weights of the model should be updated. However due to computational problems, the Negative sampling technique is implemented by training a small percentage of the weights, rather than all of them. In order to understand the way this is accomplished, it is important to recall one-hot embeddings. The outputs of the labeled word pairings in the output layer are represented as one-hot vectors. The correct outputs are encoded as 1's and the rest 0. During the training process of the neural network, the weights for all the wrong outputs along with the representation for the right output are adjusted. With negative sampling however, only the weights for a small proportion of "negative" words(words that are represented as 0) are adjusted along with the correct representation. Since only a small proportion of the weights are adjusted, the computation time is reduced.
How are the negative words sampled then? By using a method called "unigram distribution", the words that appear more frequently in a corpus are more likely to be sampled. The frequency of a certain word is divided by the the entire size of the corpus. In the adjusted sampling, the frequency is raised to the power of 3/4. This ultimately penalizes frequent words and rewards the sparsely appearing words.
- Heirarchical Soft-Max: This section is a part where I need to understand data structures better, but to sum up switching the final soft max layer to a heirarchical soft max structure(a binary tree structure) speeds up the computational time.
Up until this point, we've found a way to use neural networks to map out the words from long text using the context words surrounding a target word. This is mainly known as the Word2vec method using either CBOW or Skip-Gram. However this method holds limitations to what it can represent. Since the model only takes into account a fixed number of window words surrounding a target word, it cannont contextualize long term dependencies of words in longer sequences. This is where RNN's(Reccurrent Neural Networks) come into play.
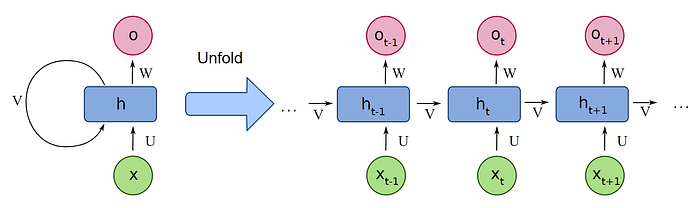
The basic structure of a vanilla RNN is like the above. For every time stamp in a sequential data structure the previous time stamps are taken into consideration when embedding the current time stamp. This process procedes until every time sequence is embedded. When put into the context of text data, which can be viewd as sequential data, the information from all previous words are put into consideration when embedding the current word.
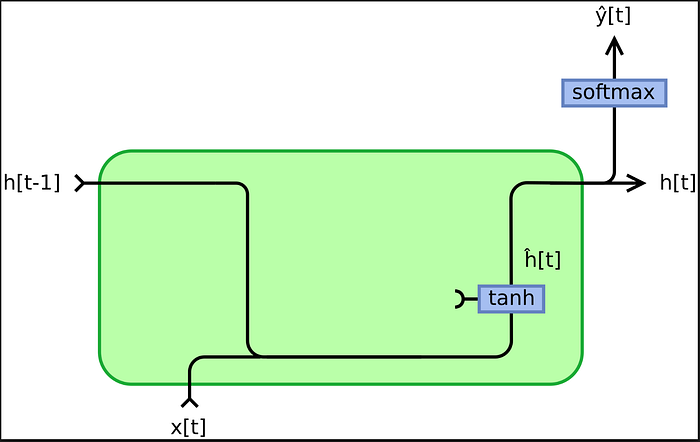
Take for example, the sentence, "I am a college student". First, the word "I" is embedded. It passes a random weight, and then a certain amount of bias is added. The embedding then passes an activation function(usually tanh) and then this information is passed on to the next word in this sequence, "am". The model takes the embedding of "I", multiplies a certain weight and then adds this value to the newly embedded "am"(this embedding passed through the same weight as the previous time stamp). The bias is taken into account and added and like the previous word "I" this value is passed on to the activation function again. This process repeats until "student" is embedded.
The optimization of this model is done by minimizing the sum of the differences between the predicted values of each time stamp(in this case the predicted words in the sentence) and the actual result this process is done by gradient descent. In the case of sentiment analysis, the data is labled in either negative or positive. The embedding of the final time stamp in a sequence is passed on to a classification layer, in this case a soft-max layer, and produces a prediction of whether the sentiment of the sequence is true or false. This is compared with the actual labelling of the word(usually labled 0 for negative, 1 for positive) and the aim is to minimize the loss.
The reason why this architecture is called a Recurrent Neural Network is because instead of passing through a feed forward network(FNN), the weights are applied with each time stamp in a sequence in a repeating manner. Unlike a FNN where different weights are applied with each layer and backpropogation happens with at the end of the passing of a dataset, an RNN uses one set of weights that is optimized with each time stamp. Thus the model is set to work in a cycling manner.