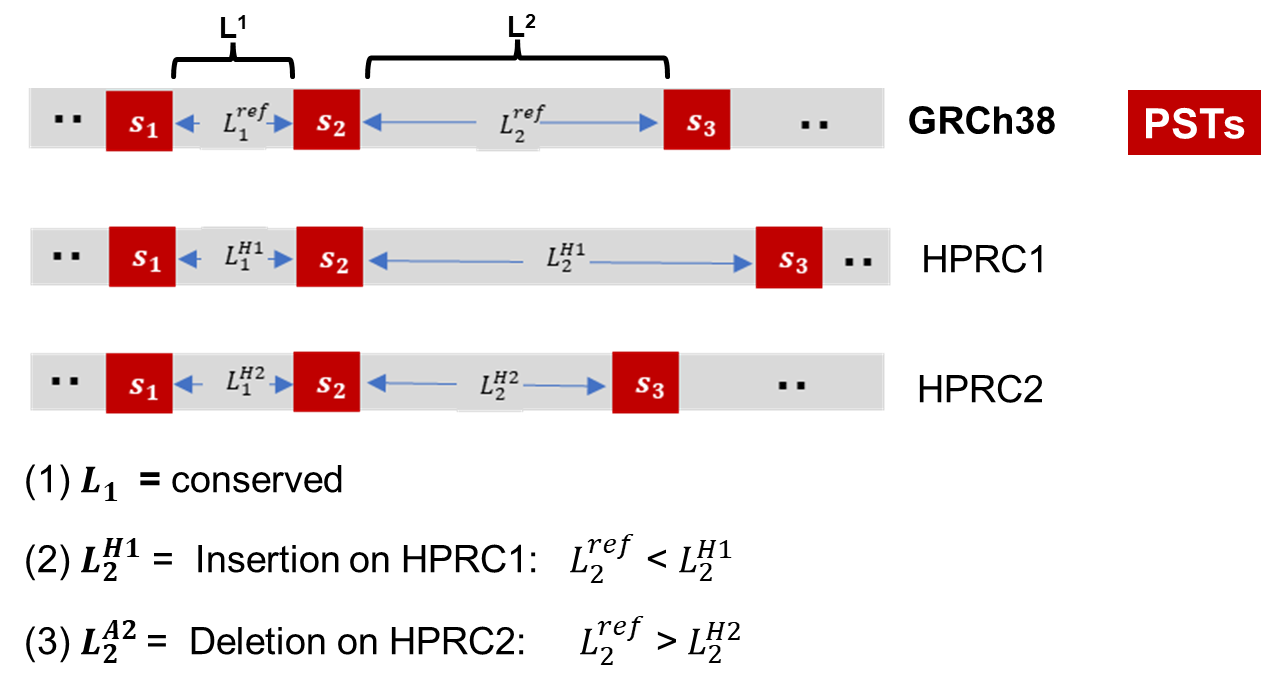
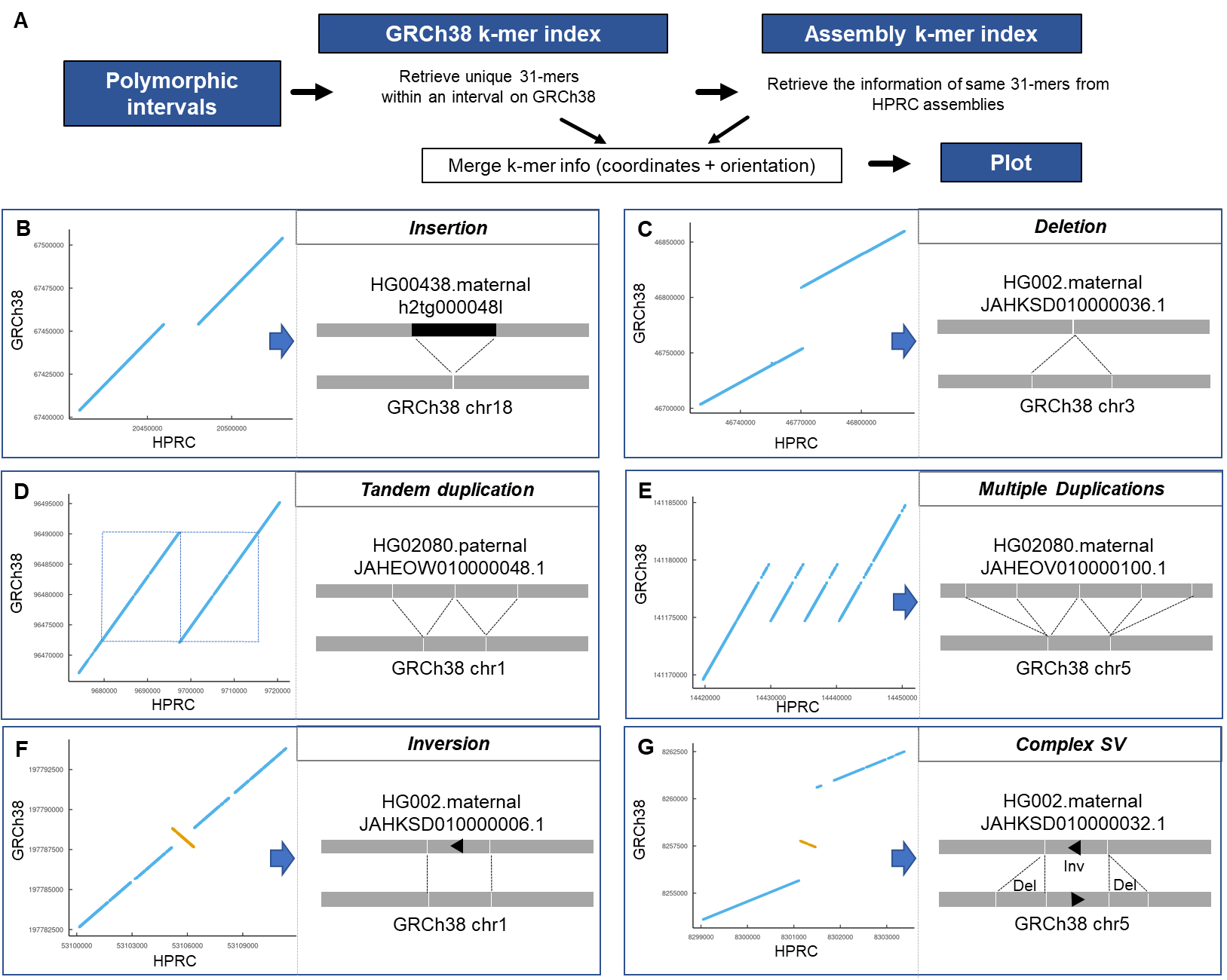
Pan-conserved tag segments provided an informative set of universally conserved sequences. Examining the intervals between pairs of these segments identified highly conserved segments of the genome versus ones that have structurally related polymorphisms.
All pan-conserved 31-mers can be downloaded in bed format, pst-31mer.grch38.bed.gz along with tbi index file, from https://dna-discovery.stanford.edu/publicmaterial/datasets/pangenome
Each row represents an interval and 13 columns in this file (see the below image)
 An interval (10052 bp) from 844891 to 854943 on chr1 on GRCh38 has the same lenght on 91 HPRC haploid assemblies. However, 3 of HPRC haploid assemblies have different interval lenghts; HG02080.paternal (345 bp shorter), HG02630.maternal (292 bp longer), HG03516.paternal (50 bp shoter) according to 12th and 13th column.
An interval (10052 bp) from 844891 to 854943 on chr1 on GRCh38 has the same lenght on 91 HPRC haploid assemblies. However, 3 of HPRC haploid assemblies have different interval lenghts; HG02080.paternal (345 bp shorter), HG02630.maternal (292 bp longer), HG03516.paternal (50 bp shoter) according to 12th and 13th column.
- The coordinates of all PSTs for 94 HPRC assemblies in addition to GRCh38
- Each file is for each chromosome. For instance, chr1.pst.hprc.bed.gz and chr1.pst.hprc.bed.gz.tbi contain all PSTs on chr1.
- These files can be used for detecting possible SVs. See below examples.
(1) all PSTs were sorted for each chromosome based on the GRCh38 coordinates using a p to q arm orientation and (2) we calculated the length of the interval sequence between any two tandem PST pairs within a given assembly contig. We conducted this process for all 94 HPRC haploid assemblies and constructed a data matrix where the columns represented a given haploid genome and the rows represented the difference in lengths between consecutive PSTs relative to GRCH38.
long psts with size of >2,500 bp. 4th column shows the length of psts.
- long conserved intervals
- the interval lengths are constant across all 94 HPRC assemblies and longer than 10 Kb
- the coordinates of PSTs across HPRC assemblies by chromosomes: chr*.pst.hprc.bed.gz (with tabix) under the directory of "pst_pos_hprc_by_chr"
- Provide the coordinates of PSTs on GRCh38 and 94 HPRC assemblies
- Use "tabix" to extract the PST within the genomic region of interest
- For retrieving exon4 of TP53 (chr17:7,661,779-7,676,594), use the following command:
tabix chr17.pst.hprc.bed.gz chr17:7,661,779-7,676,594 - information of 97 columns in chr*.pst.hprc.bed.gz:
- 1st col: chromosome on GRCh38
- 2 col: start pos on GRCh38 (0-based)
- 3rd col: end pos on GRCh38 (1-based)
- 4th col: position on HG002.maternal (i.e. JAHKSD010000079.1:2844465-2844496,+ -> contig ID:start-end,strand)
- 5th col - 97th col: the order of HPRC assemblies is in README at https://dna-discovery.stanford.edu/publicmaterial/datasets/pangenome/
- For retrieving exon4 of TP53 (chr17:7,661,779-7,676,594), use the following command:
- pst-31mer.grch38.bed.gz
- pst-31mer.grch38.bed.gz.tbi
- pan-conserved_seq.chm13.zip
- pst-31mer.chm13.bed.gz.tbi
interval_length_matrix.zip
HG002.maternal HG002.paternal HG00438.maternal HG00438.paternal HG005.maternal HG005.paternal HG00621.maternal HG00621.paternal HG00673.maternal HG00673.paternal HG00733.maternal HG00733.paternal HG00735.maternal HG00735.paternal HG00741.maternal HG00741.paternal HG01071.maternal HG01071.paternal HG01106.maternal HG01106.paternal HG01109.maternal HG01109.paternal HG01123.maternal HG01123.paternal HG01175.maternal HG01175.paternal HG01243.maternal HG01243.paternal HG01258.maternal HG01258.paternal HG01358.maternal HG01358.paternal HG01361.maternal HG01361.paternal HG01891.maternal HG01891.paternal HG01928.maternal HG01928.paternal HG01952.maternal HG01952.paternal HG01978.maternal HG01978.paternal HG02055.maternal HG02055.paternal HG02080.maternal HG02080.paternal HG02109.maternal HG02109.paternal HG02145.maternal HG02145.paternal HG02148.maternal HG02148.paternal HG02257.maternal HG02257.paternal HG02486.maternal HG02486.paternal HG02559.maternal HG02559.paternal HG02572.maternal HG02572.paternal HG02622.maternal HG02622.paternal HG02630.maternal HG02630.paternal HG02717.maternal HG02717.paternal HG02723.maternal HG02723.paternal HG02818.maternal HG02818.paternal HG02886.maternal HG02886.paternal HG03098.maternal HG03098.paternal HG03453.maternal HG03453.paternal HG03486.maternal HG03486.paternal HG03492.maternal HG03492.paternal HG03516.maternal HG03516.paternal HG03540.maternal HG03540.paternal HG03579.maternal HG03579.paternal NA18906.maternal NA18906.paternal NA19240.maternal NA19240.paternal NA20129.maternal NA20129.paternal NA21309.maternal NA21309.paternal
Here we demonstrated how we can use PSTs to identify SVs in the gene of interes.
- The coordinates of IGFN1 exons; IGFN1_exon.bed under the folder of SVs_exons (according to MANE annotation; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/MANE/)
- Generate a shell script to run tabix to grab PSTs around regions of interest
python3 cal_pst_interval_len.py enter name of your input: IGFN1_exon.bed enter search window size (recommended: 2000): 2000 enter the directory where tabix files are: ../../pst_matrix/pst_pos_hprc_by_chr/ (adjust to your path) - Calcualte the distances between selected PSTs
python3 cal_pst_interval_len.py enter output file name: IGFN1_exon_interval-len-diff.txt enter size of search window: 2000 - outcomes in IGFN1_exon_interval-len-diff.txt
- As you see in IGFN1_exon_interval-len-diff.txt, the lengths between PSTs for all exons except exon12 are identical to GRCh38.
- Interestingly, we've observed that 92 out of 94 assemblies have different lengths for exon12. For example, HG002.maternal has exon12 that are 108 bp longer, while HG002.paternal has exon12 that are 216 bp longer, when compared to GRCh38.
- We are looking for a VNTR at chr1:106430959-106431446
- Grab PSTs around this VNTR (50 bp flanking regions) using the following command:
tabix chr1.pst.hprc.bed.gz chr1:106430909-106431496 >vntr.out - Specifically, the first and last (or 4th) lines of vntr.out (under example_outcomes) provide the lengths of PSTs covering this VNTR across 94 HPRC assemblies.
- As an example, the length of this region is 568 bp on GRCh38. However, on both HG002.maternal and HG002.paternal, it is 798 bp, which is 230 bp longer than on GRCh38. The assembly IDs for columns 4 to 97 can be found in "6. Order of assemblies in the matrix files" (see above)
We identified 60,763 polymorphic invervals and use the constituent 31-mers of SVs to visualize the structure of different classes of SVs including insertions, deletions, duplications, inversion and more complex rearrangements. This process involved using a simple dot matrix plot with the two axis representing the GRCh38 and the specific haploid assembly. We plotted the position of the 31-mers that spanned the divergent interval.
Move to the "test" directory and run the following command:
for file in *merged.txt; do ../make_kmer_plot_query.R $file; done
There are total of 6 input files for 6 different types of SVs (Figure 4 in our preprint: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.10.06.511239v2)