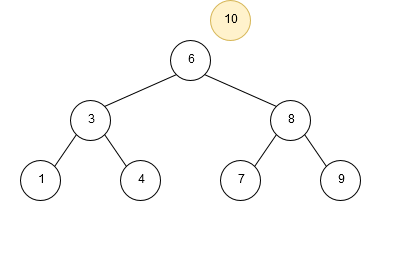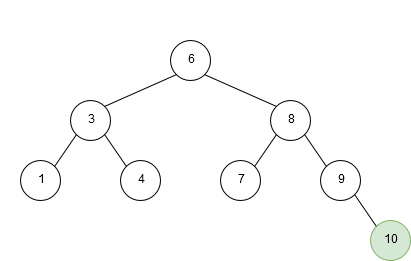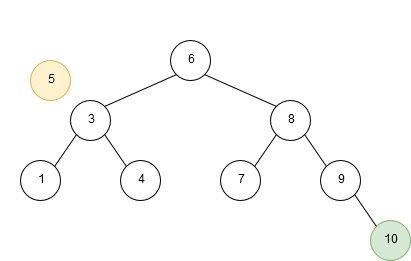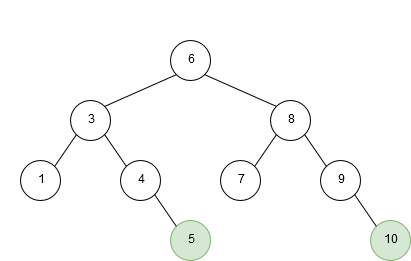
This project contains implementations of the sorting algorithms Bubble sort, Merge sort, Quick sort and Binary Tree. These algorithms were developed using the Java programming language and includes the practice of many features.
This project is still in development and I intend to have both iterative and recursive solutions for all algorithms in the future. Another future aim is to add an improved GUI application to provide users with a simple experience whilst showing the algorithms in action. Allowing users to use more of the implemented functions in the console such as retrieving the left and right node of an element in a binary tree. Finally, I intend to include Generics inside this application.
- JUNIT: Used to test each sorting algorithm against multiple conditions, ensuring correct outputs and also including performance tests.
- SOLID Principles: This project abides by the SOLID principles to follow clean code practices and allow extensibility
- ENUMS: Enums helped to avoid errors and ensure the correct sorting algorithm was initiated
- Nested Classes: Used for the Node class inside the Binary Tree class, as no other class required the use of the Node class.
- Exceptions: Created custom exceptions such as ChildNotFound and ArrayEmpty
- Logging: Used the Log4j utility tool to log errors
This simple sorting algorithm is a comparison based algorithm. Operating by comparing each element in a list to the adjacent element value to derive which element is out of order and swapping their positions. This algorithm continues until the whole list is ordered. Bubble sort is not suitable for large data sets as the average and worst case time complexity is O(n^2) - n is the size of the list.
Merge sort is an algorithm based on the divide and conquer technique. Sorting a list by first dividing it into multiple single element lists, and then mergeing all lists in a sorted manner - hence Merge sort. Merge sort performs better than bubble sort when large data sets are involved, with a worst-case time complexity of O(n log n).
Like Merge sort, the Quick sort algorithm is also a divide and conquer technique. Sorting a list by partitioning it into smaller lists. A value in the list is selected as the pivot to divide the list by which values are less than the pivot and which values are greater than the pivot. Quick sort is highly efficient with large data sets, having an average and worst-case time complexity of O(n^2).
A Binary Tree contains multiple elements (usually known as Nodes), which have up to a maximum of 2 child Nodes (leafs). The right child Node represents the value(s) that is greater than the current (parent) Node, and the left child Node represent the value(s) less than the current Node. When adding a new element the value is compared to the root Node first and procedes to traverse through the Tree until it reaches an empty (null) child Node.