In this project we connect to the FlightGear Simulator (fgfs) and provide it with a set of pre-recorded measurements of an airplanes instruments to simulate the original flight. We also show a variety of the airplane's instruments such as altitude, airspeed, pitch-roll-yaw degrees, aileron, elevator and rudder in real-time on the screen.
Special features
There's additional features in the project:
- When we click on points on the graph the playback jumps to specific episode and starts to play from this moment.
- There's a red vertical line moving on graphs showing the location of current points in accordance with the playing playback.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vH_aki95r3I
In this project we're using:
- .NET Framework to create a GUI Application.
- MVVM architectural pattern in a multi-threaded environment.
- TCP protocol for communication with the FlightGear Simulator.
The program takes a CSV file containing the recorded flight's measurements.
We created an on-screen control unit, which includes:
- Joystick that recreates the movement of the on-plane joystick.
- Dashboard to display the numerical data sent from the airplane.
- Graph Control to display all of the flight's features in a time graph, along with their most correlative feature.
- Graph Regression displaying each two correlative features along with their linear regression line (and other shapes).
- Video Control to control the recorded flight - play, pause, fast-forward or backward and change playing speed, making the simulator come to live.
The app takes a user-specified anomaly detection algorithm. We supplied 2 in the plugin folder - linear and circular based, written in C++. We wrapped this C++ code with a dll (Dynamic Link Library) and loaded it to our current project. Any developer can add a new anomaly detection algorithm of his own, by implementing the provided interface - IAnomalyDetector.
The files we load to simulator are:
- An XML file to define which of the plane's instrument each column in the CSV represents.
- One file is a normal and regular flight containing all necessary flight's details. We're using this file and with our DLL to learn what a 'correct' flight is.
- Second file is an input flight for the anomaly detection proccess. The app will search for anomalies in this flight, based on what we learned before.
We provide the first two as default and the user provides the third one.
In branch 'master' we have these files:
Contains the C++ files from the first semester, responsible for the learning phase.
Explanation follows after files' description.
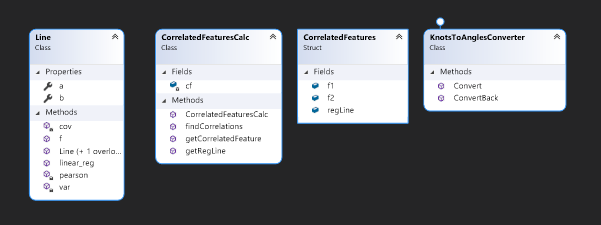
CorrelatedFeaturesCalc.cs - By providing a file name, this class uses the before mentioned DLL to find correlated features.
DataFileReader.cs - The DataFileReader object receives the CSV file to be read, and reads it line-by-line. It notifies all of its listeners about the progress, allowing them to ask it for the new information at every step.
Line.cs - Line represented by a slope and a Y-axis intersection point (ax+b).
MainViewModel.cs - The main ViewModel of the application. All of the components are subscribed to the MainViewModel according to the MVVM architecture. The also MainViewModel forwards the DataFileReader notifications and controls the requests for the this data.
MainWindow.xaml.cs - The main view that contains all the controls components and displays them.
playback_small.xml - The XML definitions file for the flight simulator.
The client that connects to the flight simulator server and send it the data read by DataFileReader (at 10Hz).
Images for the controls.
Contains all the Controls of the project.
Explanation of the controls:
DashBoard
The main role of the Dashboard is visually displaying the numerical data sent from the airplane. It contains the view and viewModel. The viewModel is listening to MainViewModel. It also implements ViewModel abstract class.
In addition there's a class KnotsToAnglesConverter that converts the knots to angles using scaling calculations to visually represent the data with a radial gauge.
GraphControl
Graph Control to display flight's features in a time graph. Contains a view that is bound to the MainViewModel.
GraphReg
A Graph displaying pairs of correaltive features, one as afunction of the other, based on the pre-learned correlation analysis. It also calculates the linear regression line for those features and displays it. It contains view and viewModel. The viewModel is listening to the MainViewModel. It also implents the ViewModel abstract class.
Joystick
Joystick that uses the aileron and elevator to recreate the movement of a real in-flight joystick. Also shows rudder and throttle levels. Contains view, viewModel and model. The viewModel is listening to MainViewModel and implents the ViewModel abstract class.
VideoControl
Video Control main role is to play the recorded flight making the simulator interactive. It contains view, viewModel and model. The viewModel is listening to MainViewModel. It also implents the ViewModel abstract class.
***ViewModel.cs ***
The abstract class for the ViewModels. It containts the MainViewModel as a member and implents the INotifyPropertyChanged interface.
Contains images of the UMLs chart.
Contains images to display in README.md file.
Plugins to load into the project as DLLs and the flight csv file to be inspected.
- Visual Studio 2019
- .NET desktop development
- .NET development with C++
- C++/CLI support for v142 build tools
System requirements:
- .NET Framework
- Microsoft.SDK.Expression.Blend
Downloading and Installing Flight Gear: https://www.flightgear.org/download/
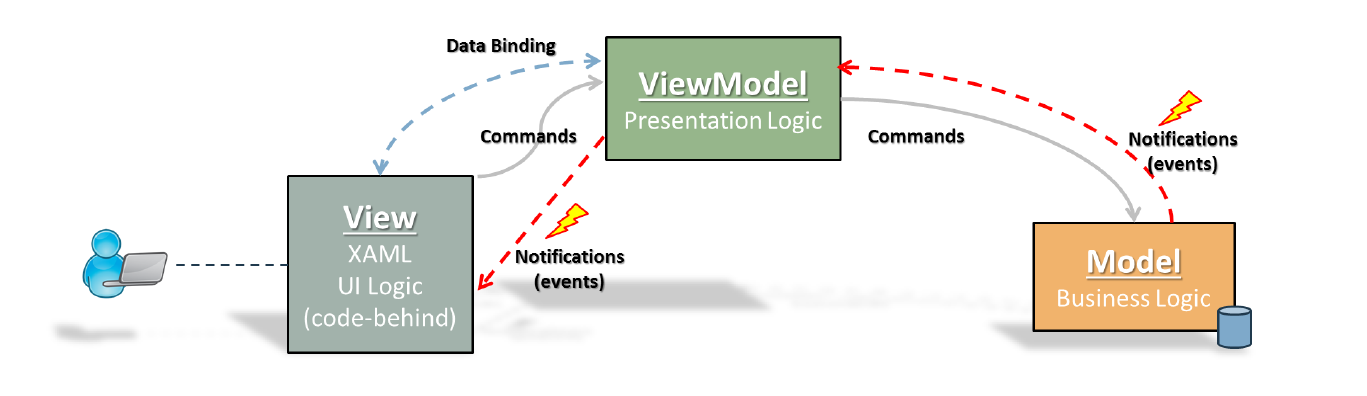
In our project we used MVVM architecture in order to make everything work.
The MVVM architectural pattern is divided to three parts: View: responsiple for the visual display of the data to the user. ViewModel: manages between the View and the Model. Model: contains the algoritim to proccess the data for displaying. We are using Data Binding Between the View and the ViewModel. So when a proprety has been changed in the view (i.e user selected a feature to display), it will change an appropriate to the value that is bound to this proprety. The View send Commands to the ViewModel that passes those commands to the Model. View gets notfications from the ViewModel if he listens. The ViewModel also get notfications but from the model for what he listens.
The views - GraphReg, Joystick, VideoControl, Dashboard and MainWindow passing commands to their viewModels, and get notified accordingly from the viewModel. That way we bind user interface objects to viewModel, so the connection between view and viewModel is bidirectional.
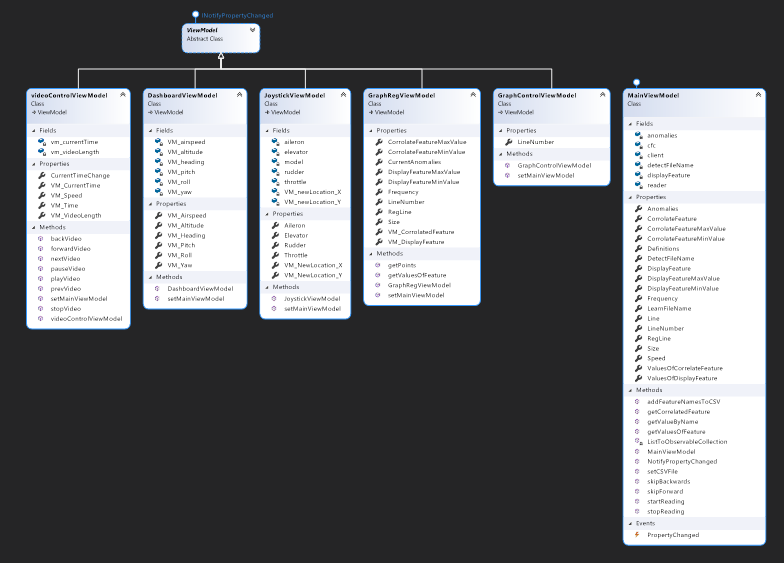
VideoControlViewModel, DashBoardViewModel, JostickViewModel, GraphControlViewModel and GraphRegViewModel extends the abstract class ViewModel that Implents the InotifyPropretyChanged. The ViewModel contains the MainViewModel, and the mentioned ViewModels above contains it as well because they extend ViewModle. Each ViewModel Above listens according to the MVVM architecture to the MainViewModel. The MainView Model listens to the DataFileReader(Model) also according to the MVVM architecture.
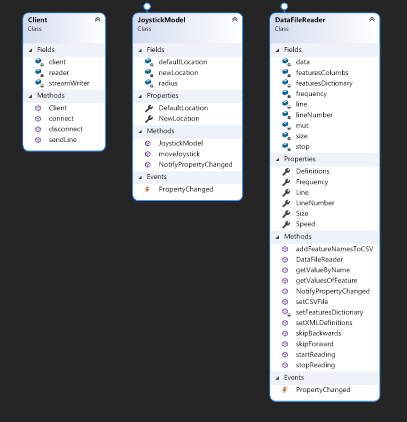
Each Model has it's own algoritm that works according to its specific logic. Client - connects to the flight gear simulator and sends data according to the DataFileReader its listening to by MVVM architecture. JoystickModel - responsible for the Joystick algorithm. DataFileReader - the main algorithm of our project, manages almost everything.
CorrelatedFeatureCalc- class with methods that calculate the correlated features in the specific flight, this features will be displayed in appropriate graphs.
KnotsToAnglesConverter- in order to display the speed in knots on radial gauge control we had to scale it with appropriate calculations.
Line- class that defines a line for line-regression graph. The correlated features will be represented as axis x and axis y. The scattered data points will be displayed around linear regression line
CorrelatedFeatures- class of CorreleatedFeatures consists of any two chosen correlated features and their linear regression line
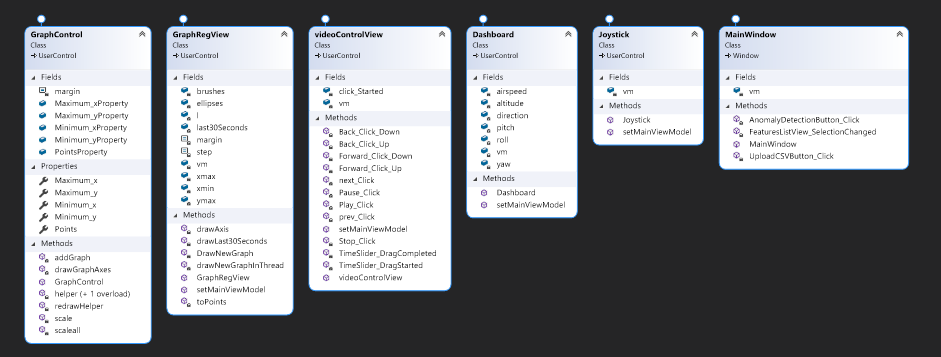
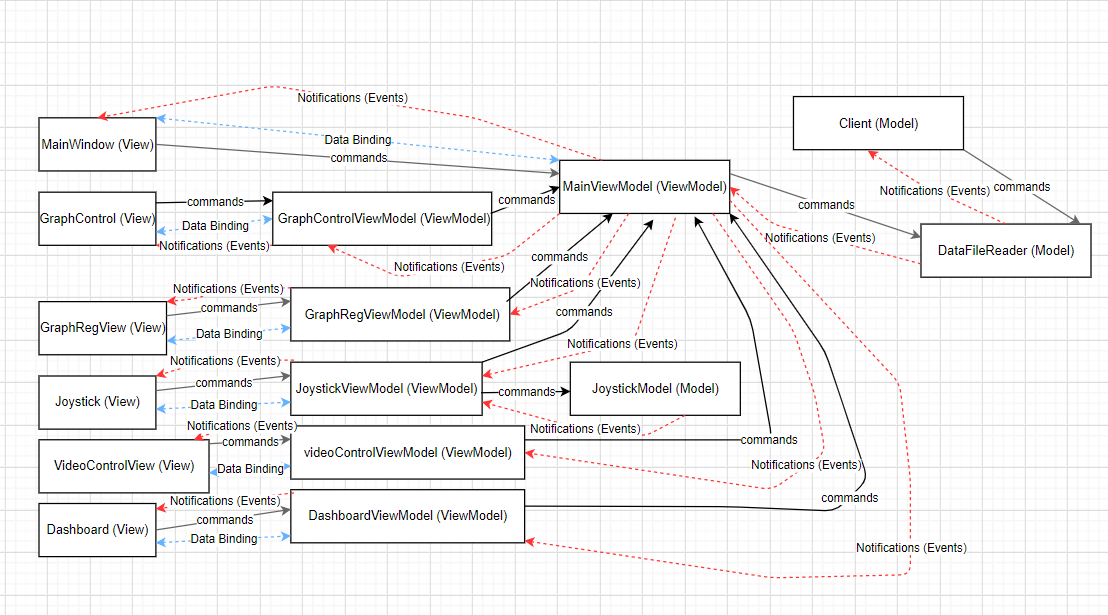
Explanation for the diagram attached above:
- The GraphReg, Joystick, ViewControl and Dashboard views are all work with their ViewModels.
- The MainWindow and GraphControl views plus GraphReg, Joystick, ViewControl and Dashboard ViewModles are all works with the MainViewModel.
- The joystick also has his own Model.
- The MainViewModel and the client work together with the DataFileReader.
- The flow of the data is happening that way: views -> ViewModels -> MainViewModel -> DataFileReader(Model) (with commands and binding), Client -> DataFileReader(Model). in the opposite way, they get notified from DataFileReader(Model) -> MainViewModel and Client -> ViewModels -> Views.