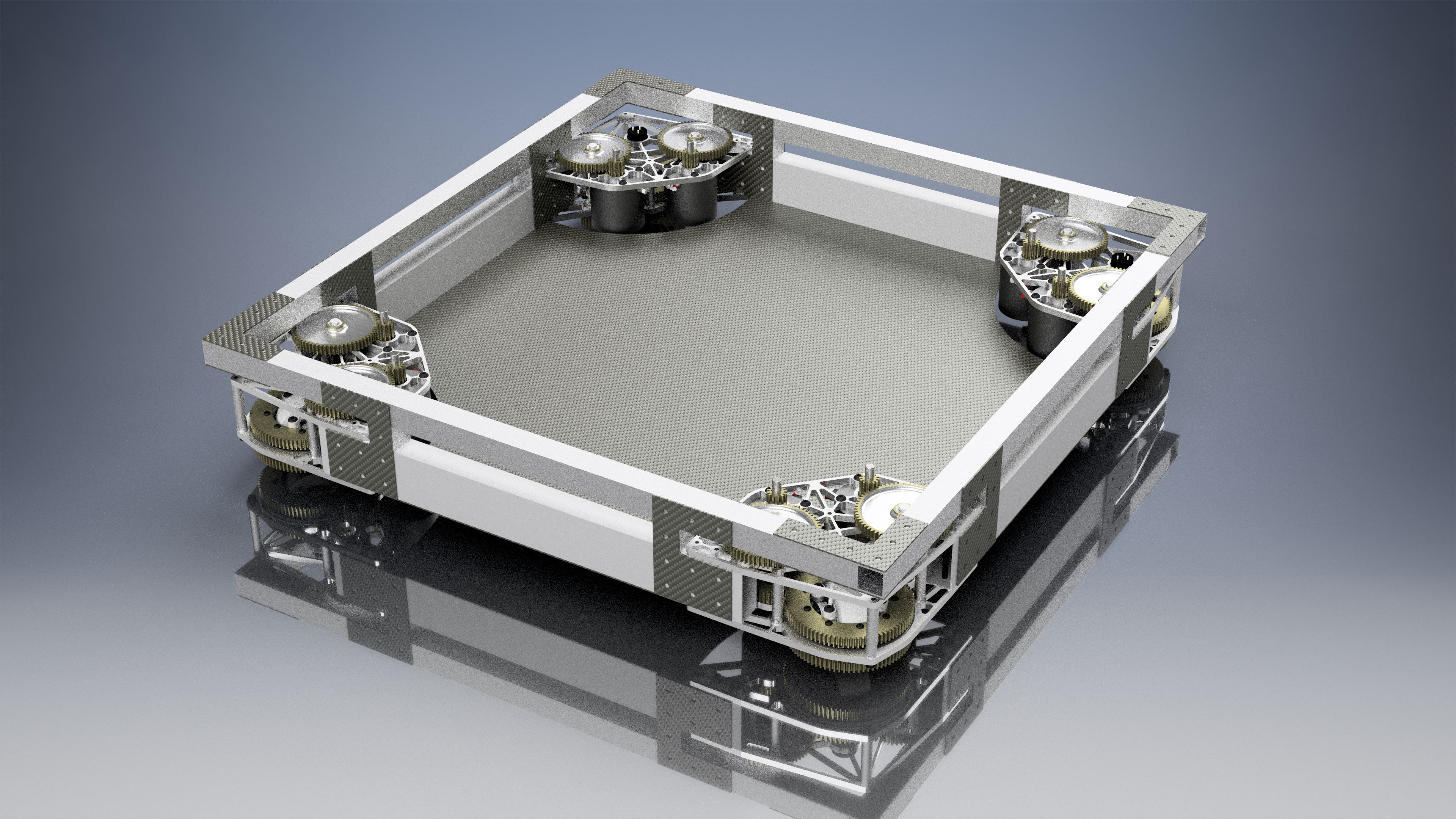
A comprehensive swerve drive template for FRC robots written in Kotlin, featuring advanced logging, vision processing, and autonomous capabilities.
- Overview
- Features
- Project Structure
- Dependencies
- Setup and Installation
- Configuration
- Usage
- Subsystems
- Commands
- Autonomous
- Development Tools
- Contributing
- License
This repository contains a production-ready swerve drivetrain template for FRC Team 4079. The codebase is built using Kotlin and integrates modern FRC development practices including advanced telemetry logging with AdvantageKit, computer vision with PhotonVision, and sophisticated path planning capabilities.
- Swerve Drive Implementation: Full 4-module swerve drive with CTRE Phoenix 6 motor controllers
- Advanced Logging: Comprehensive telemetry and replay capabilities using AdvantageKit
- Computer Vision: PhotonVision integration for target detection and robot localization
- Path Planning: PathPlanner integration for autonomous navigation
- LED Control: Programmable LED strip control for status indication
- Controller Support: Xbox controller integration with customizable button mappings
- Code Quality: Automated formatting with Spotless and documentation generation with Dokka
src/main/java/frc/robot/
├── Robot.kt # Main robot class with AdvantageKit logging
├── RobotContainer.kt # Robot configuration and command bindings
├── Main.java # Application entry point
├── commands/ # Robot commands
│ ├── AlignSwerve.kt # Swerve alignment command
│ ├── Kommand.kt # Command factory and utilities
│ └── PadDrive.kt # Gamepad driving command
├── subsystems/ # Robot subsystems
│ ├── LED.kt # LED strip control
│ ├── PhotonModule.kt # PhotonVision camera module
│ ├── PhotonVision.kt # Vision processing subsystem
│ ├── Swerve.kt # Main swerve drive subsystem
│ └── SwerveModule.kt # Individual swerve module
└── utils/ # Utility classes
├── Dash.kt # Dashboard utilities
├── Direction.kt # Direction enumeration
├── PIDVController.kt # Enhanced PID controller
├── RobotParameters.kt # Robot configuration constants
└── controller/ # Controller input handling
├── Axis.kt
├── Button.kt
├── GamingController.kt
└── Trigger.kt
- WPILib 2025: Core FRC library framework
- Kotlin JVM: Primary programming language
- CTRE Phoenix 6: Motor controller and sensor library
- AdvantageKit: Advanced logging and replay system
- PhotonVision: Computer vision library
- PathPlanner: Path planning and autonomous library
- GradleRIO: Build and deployment system
- Spotless: Code formatting and style enforcement
- Dokka: Kotlin documentation generation
- JUnit 5: Unit testing framework
- Java 17 or higher
- WPILib 2025 installation
- Git
- Clone the repository:
git clone <repository-url>
cd SwerveBaseTemplate- Build the project:
./gradlew build- Deploy to robot:
./gradlew deployKey configuration values are centralized in RobotParameters.kt:
- Motor CAN IDs: Drive and steer motor controller IDs
- Swerve Kinematics: Wheel positions and module configurations
- PID Constants: Tuning parameters for drive and steer controllers
- Physical Constants: Robot dimensions, gear ratios, and wheel specifications
Autonomous paths and autos are stored in src/main/deploy/pathplanner/:
paths/: Individual path segmentsautos/: Complete autonomous routinessettings.json: Global PathPlanner settings
- Left Stick: Translational movement (X/Y)
- Right Stick: Rotational movement
- Button A: Reset gyroscope heading
- Button B: Enable/disable field-relative driving
- Start Button: Switch to teleop PID mode
Autonomous routines are selectable via NetworkTables dashboard chooser. Available autos include:
- 4l4auto: Four-piece autonomous routine
- Straight Auto: Simple forward movement
- Test Auto: Basic functionality test
- Four-module swerve drive using CTRE TalonFX motors
- Absolute position feedback via CANcoders
- Field-relative and robot-relative drive modes
- Automatic module optimization for shortest rotation path
- Multi-camera support for AprilTag detection
- Robot pose estimation and field localization
- Integration with swerve drive odometry
- Programmable LED strip control
- Status indication for robot states
- Customizable color patterns and effects
- PadDrive: Primary teleop driving with gamepad input
- AlignSwerve: Automated alignment to vision targets
- resetPidgey: Reset gyroscope heading to zero
- setTelePid: Configure PID controllers for teleop mode
The robot supports PathPlanner-based autonomous routines with:
- Pre-planned paths with custom constraints
- Event-based command execution during path following
- Real-time path visualization in simulation
- Spotless: Automatic code formatting on build
- Dokka: Generate comprehensive API documentation
- JUnit: Unit testing framework for validation
- AdvantageKit: Record all robot data for post-match analysis
- Replay Mode: Re-run robot code with recorded data
- Network Tables: Real-time data visualization
./gradlew build # Build project
./gradlew deploy # Deploy to robot
./gradlew simulateJava # Run robot simulation
./gradlew replayWatch # Watch replay files- Follow the existing code style (enforced by Spotless)
- Add appropriate documentation for new features
- Test changes thoroughly in simulation before deployment
- Update this README when adding significant features
This project is licensed under the terms of the WPILib License. See the WPILib-License.md file for details.