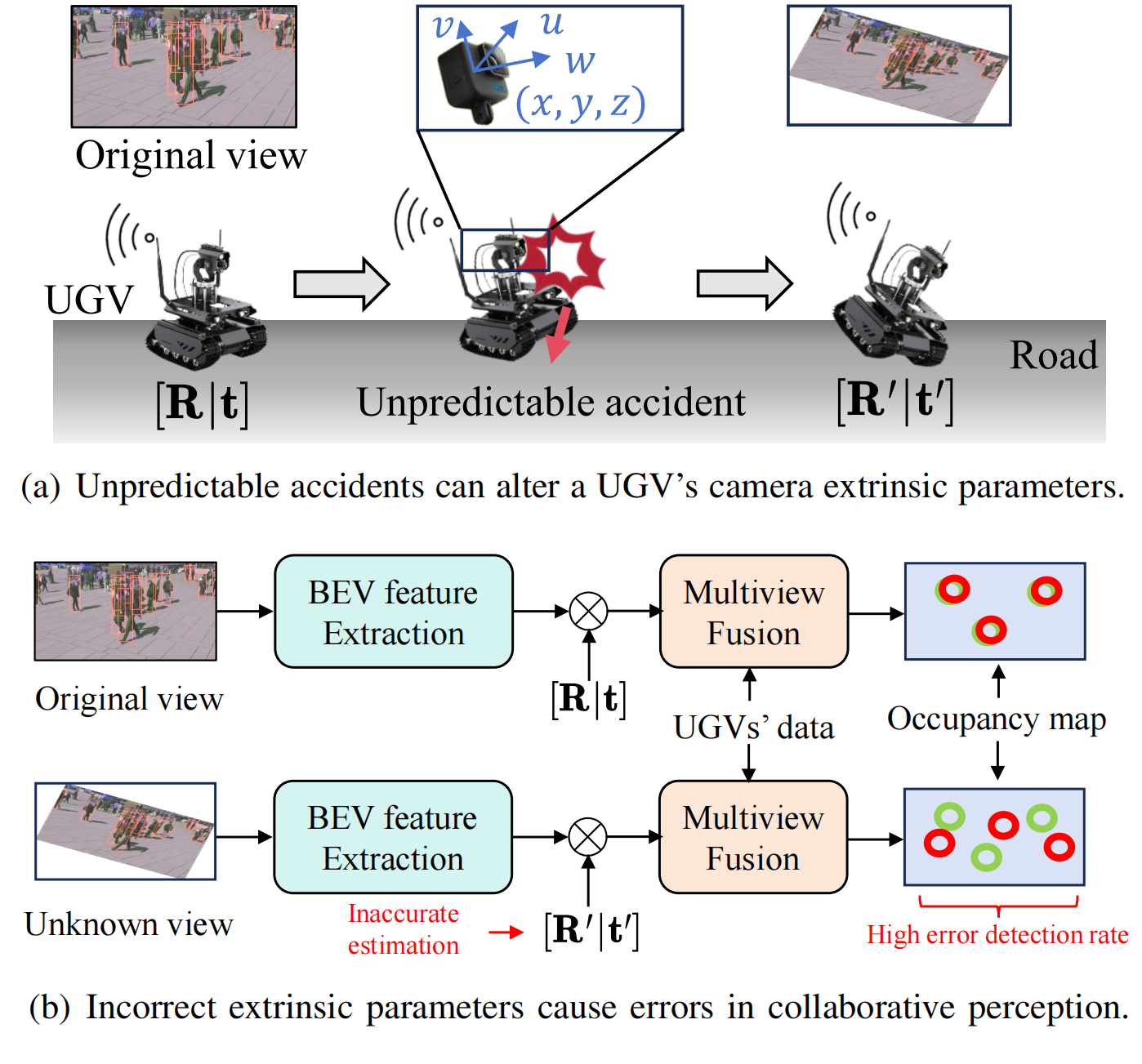
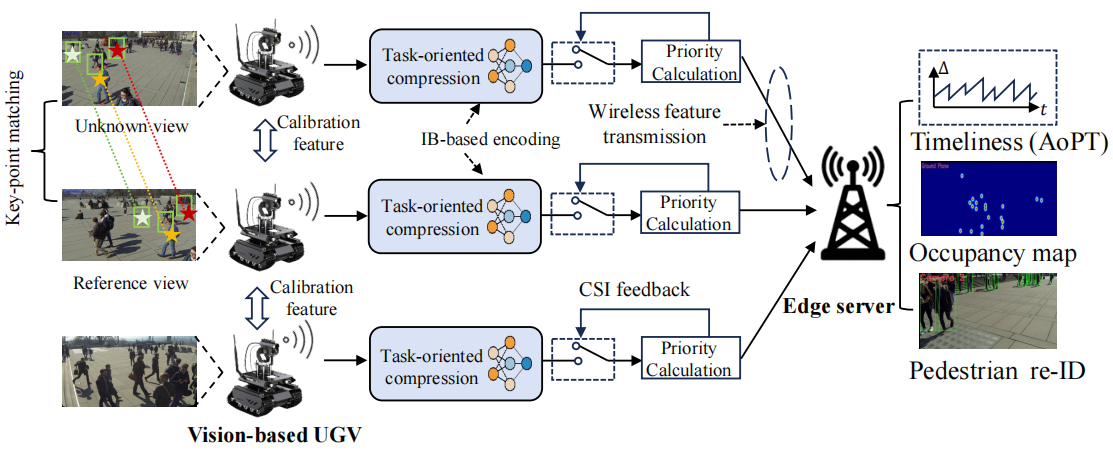
In collaborative perception systems, multiple unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) equipped with cameras work together to enhance sensing capabilities and perception accuracy. However, dynamic environments pose significant challenges:
- Extrinsic Calibration Errors: Sudden movements, accidents, or terrain changes frequently disrupt camera calibration parameters, causing perception inaccuracies.
- Timeliness and Data Freshness: Ensuring real-time updates and fresh data streams is essential, especially in scenarios requiring timely reactions (e.g., pedestrian tracking, emergency alerts).
- Communication Constraints: Bandwidth limitations and unreliable communication channels further complicate real-time collaborative perception.
Figure 1 illustrates how unpredictable accidents involving UGVs impact extrinsic calibration parameters, significantly increasing perception errors.
- Re-ID Based Feature Matching: Uses pedestrian re-identification for robust key-point matching
- Adaptive Quantization: Adjusts feature precision based on channel quality
- Real-time Calibration: No need for calibration targets or manual intervention
- Task-Oriented Encoding: Compresses features while preserving task-relevant information
- Temporal Correlation: Leverages frame-to-frame correlations to reduce redundancy
- Dynamic Rate Adjustment: Adapts compression rates based on channel conditions
- Dynamic Packet Loss Handling: Maintains performance under severe packet loss (up to 40%)
- Feature Prioritization: Assigns importance scores to different camera features
- Adaptive Masking: Selectively drops less important features during transmission
The system consists of multiple UGVs equipped with edge cameras that collaboratively track pedestrians, transmitting decoded feature streams to an edge server through wireless channels for comprehensive occupancy mapping and real-time calibration.
- MODA (Multiple Object Detection Accuracy): Primary perception accuracy metric
- Communication Cost: Measured in KB, representing transmission overhead
- AoPT (Age of Perceived Targets): Novel metric combining data freshness and target relevance
- Calibration Error: Rotation and translation errors in camera extrinsic parameters
The R-ACP framework consists of three main components:
R-ACP/
├── main_coding_and_inference.py # Main training and inference script
├── Camera_calibration/
│ └── main-multi-gpu.py # Re-ID based camera calibration
├── multiview_detector/
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── persp_trans_detector.py # Core perception model with calibration
│ │ └── Priority_network.py # Priority-aware feature selection
│ ├── datasets/ # Dataset handling
│ ├── loss/ # Loss functions
│ └── utils/ # Utility functions
├── models/ # Pre-trained model storage
├── models_temp/ # Temporary model storage
├── temp/Calibration/ # Calibration error simulation data
└── README.md
main_coding_and_inference.py: Main training and inference pipeline that coordinates the entire R-ACP frameworkCamera_calibration/main-multi-gpu.py: Re-ID based calibration implementation with multi-GPU supportpersp_trans_detector.py: Core perception model implementing:- Multi-view feature extraction and fusion
- Real-time camera calibration with error simulation
- Information Bottleneck-based compression
- Temporal correlation modeling
Priority_network.py: Lightweight priority network for adaptive feature selection under packet loss conditions
To replicate the environment and dependencies used in this project, you will need the following packages:
# Core dependencies
kornia==0.6.1
matplotlib==3.5.3
numpy==1.21.5
pillow==9.4.0
python==3.7.12
pytorch==1.10.0
torchaudio==0.10.0
torchvision==0.11.0
tqdm==4.66.4
pandas>=1.3.0
opencv-python>=4.5.0
# Re-ID and calibration dependencies
torchreid>=1.3.0
ultralytics>=8.0.0 # For YOLOv5
scipy>=1.7.0 # For entropy calculations# Create conda environment
conda create -n MVDet_NEXT python=3.7.12
# Activate environment
conda activate MVDet_NEXT
# Install PyTorch and dependencies
conda install pytorch==1.10.0 torchvision==0.11.0 torchaudio==0.10.0 -c pytorch
# Install additional requirements
pip install kornia==0.6.1 matplotlib==3.5.3 numpy==1.21.5 pillow==9.4.0 tqdm==4.66.4 pandas opencv-python
# Install Re-ID and calibration dependencies
pip install torchreid ultralytics scipy
# Download YOLOv5 pre-trained model (will be downloaded automatically on first run)
# Download OSNet model for Re-ID (will be downloaded automatically on first run)Our experiments employ the Wildtrack dataset from EPFL. This dataset features high-resolution images captured by seven cameras positioned in an urban environment, recording natural pedestrian trajectories [Chavdarova et al., 2018]. Download the Wildtrack dataset and organize it as follows:
/Data/Wildtrack/
├── Image_subsets/
│ ├── C1/
│ ├── C2/
│ ├── C3/
│ ├── C4/
│ ├── C5/
│ ├── C6/
│ └── C7/
├── annotations_positions/
└── calibrations/
Before running the main collaborative perception system, you can perform initial camera calibration using the Re-ID based method:
# Navigate to calibration directory
cd Camera_calibration
# Run Re-ID based calibration with default settings
python main-multi-gpu.py
# Or modify parameters in the script:
# reference_camera_id = 1 # Reference camera ID
# unknown_camera_id = 7 # Camera to calibrate
# N_threshold = 5 # Number of matching pairsThis will generate:
- XML log files with foot center coordinates
- Communication cost analysis
- Feature matching results
# Navigate to project directory
cd /path/to/R-ACP
# Activate conda environment
conda init
source activate
conda activate MVDet_NEXT
# Copy pre-trained model (if available)
cp models/MultiviewDetector.pth models_temp/MultiviewDetector.pth
# Run training and inference
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3 python main_coding_and_inference.py \
--dataset_path "/Data/Wildtrack" \
--model_path "./models_temp/MultiviewDetector.pth" \
--epochs 30 \
--tau_1 2 \
--tau_2 2 \
--drop_prob 0.7--dataset_path: Path to the Wildtrack dataset--model_path: Path to pre-trained model (leave empty for training from scratch)--epochs: Number of training epochs (default: 10)--batch_size: Batch size for training (default: 1)--lr: Learning rate (default: 0.1)
--tau_1: Temporal fusion window size for collaborative perception (default: 0)--tau_2: Temporal entropy modeling window size (default: 1)--drop_prob: Packet drop probability for robustness testing (default: 0.1)--cls_thres: Classification threshold (default: 0.4)
The R-ACP framework includes two main calibration components:
The main-multi-gpu.py script implements the Re-ID based calibration method for real-time camera extrinsic parameter estimation:
# Navigate to calibration directory
cd Camera_calibration
# Run Re-ID based calibration
python main-multi-gpu.pyKey Features:
- Multi-GPU Support: Utilizes multiple GPUs (0-3) for parallel processing
- Pedestrian Detection: Uses YOLOv5 for real-time person detection
- Feature Extraction: Employs OSNet for robust re-identification features
- Communication Cost Analysis: Calculates entropy-based transmission costs
Configuration Parameters:
reference_camera_id = 1 # Reference camera for calibration
unknown_camera_id = 7 # Camera to be calibrated
N_threshold = 5 # Number of matching pairs to consider
frame_start = 0 # Starting frame number
frame_end = 2000 # Ending frame number
frame_step = 5 # Frame sampling intervalOutput:
- XML log files with foot center coordinates in
./24-JSAC/Re_ID_Test/match_log/ - Matched images in
./24-JSAC/Re_ID_Test/match_image/ - Communication cost metrics for each frame
The main framework automatically simulates calibration errors during testing phase (after epoch 10). Error parameters are read from:
/temp/Calibration/calibration_test_rotation_error.csv
This CSV should contain columns:
Epoch: Current epoch numberTranslation Error: Translation error magnitudeRotation Error: Rotation error magnitudeerror_camera: Comma-separated list of camera indices to apply errors
The R-ACP system operates in three phases:
- Phase 0 (Idle): No targets detected, minimal communication
- Phase 1 (Calibration): Camera recalibration using Re-ID based method
- Phase 2 (Streaming): Active target tracking with adaptive compression
During execution, the system will:
- Save training logs to
logs/directory with timestamp - Output current epoch to
epoch.log - Generate perception maps in
/temp/map_res/ - Display MODA (Multiple Object Detection Accuracy) and communication cost metrics
Training...
Testing...
maximum_MODA is 85.23%, minimum_bits_loss 12.45 KB
Epoch: 15, Reading CSV for test parameters...
Applied translation error 0.05 and rotation error 0.02 to cameras [1, 3]
For systems with limited GPU memory:
# Use single GPU
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python main_coding_and_inference.py [args]
# Reduce batch size
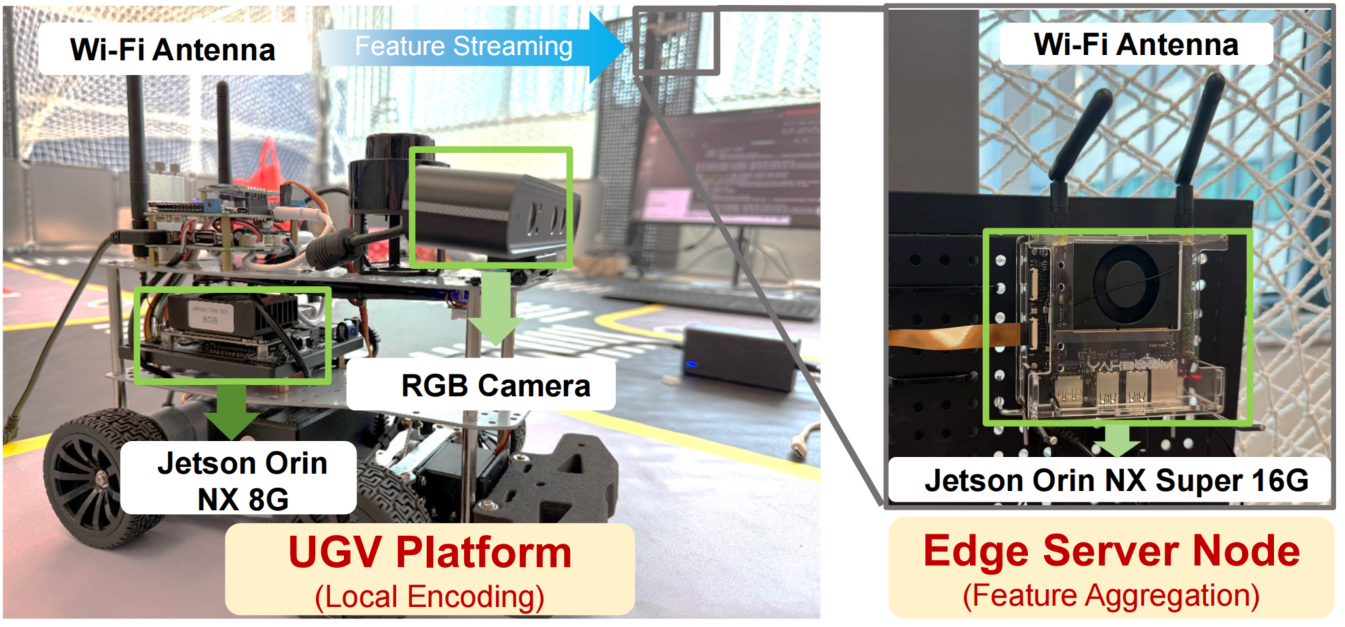
python main_coding_and_inference.py --batch_size 1 [other args]Our R-ACP framework has been validated on a real hardware testbed consisting of multiple UGVs and edge devices:
Hardware Configuration:
- Multiple UGV Platforms: Each equipped with Jetson Orin NX 8G computing units and RGB cameras for local feature encoding
- Multiple Edge devices: Powered by the latest Jetson Orin NX Super 16G and Raspberry Pi 5 16GB for feature aggregation and collaborative perception
- Wi-Fi Communication: Wireless feature streaming between UGV nodes and edge server
- Real-time Processing: Supports real-time collaborative perception with hardware-accelerated inference
This physical implementation demonstrates the practical feasibility of R-ACP in real-world scenarios, validating our theoretical framework under actual communication constraints and computational limitations.
If you use this code in your research, please cite:
@article{Fang2025RACP,
author = {Zhengru Fang and Jingjing Wang and Yanan Ma and Yihang Tao and Yiqin Deng and Xianhao Chen and Yuguang Fang},
title = {{R-ACP: R}eal-Time Adaptive Collaborative Perception Leveraging Robust Task-Oriented Communications},
journal = {IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications},
year = {2025},
month = {June},
publisher = {IEEE}
}Please find our related work about collaborative perception:
@article{fang2025ton,
title={Prioritized Information Bottleneck Theoretic Framework with Distributed Online Learning for Edge Video Analytics},
author={Fang, Z. and Hu, S. and Wang, J. and Deng, Y. and Chen, X. and Fang, Y.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Networking},
year={Jan. 2025},
note={DOI: 10.1109/TON.2025.3526148},
publisher={IEEE}
}
@ARTICLE{fang2025tmc-pacp,
author={Fang, Zhengru and Hu, Senkang and An, Haonan and Zhang, Yuang and Wang, Jingjing and Cao, Hangcheng and Chen, Xianhao and Fang, Yuguang},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing},
title={{PACP: P}riority-Aware Collaborative Perception for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles},
year={2024},
volume={23},
number={12},
pages={15003-15018},
publisher={IEEE}
}We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of the following projects:
- MVDet for their invaluable tools and insights into multi-view detection.
- TOCOM-TEM for providing task-oriented communication framework for edge video analytics.
For questions and support, please contact:
- Zhengru Fang: [email protected]
- Project Repository: github.com/fangzr/R-ACP