diff --git a/.readthedocs.yaml b/.readthedocs.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ca009ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.readthedocs.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+# .readthedocs.yaml
+# Read the Docs configuration file
+# See https://docs.readthedocs.io/en/stable/config-file/v2.html for details
+
+# Required
+version: 2
+
+# Set the version of Python and other tools you might need
+build:
+ os: ubuntu-22.04
+ tools:
+ python: "3.10"
+ # You can also specify other tool versions:
+ # nodejs: "16"
+ # rust: "1.55"
+ # golang: "1.17"
+
+# Build documentation in the docs/ directory with Sphinx
+sphinx:
+ configuration: docs/conf.py
+ fail_on_warning: true
+
+# If using Sphinx, optionally build your docs in additional formats such as PDF
+# formats:
+# - pdf
+
+# Optionally declare the Python requirements required to build your docs
+python:
+ install:
+ - requirements: docs/requirements.txt
+ - requirements: requirements.txt
+ - method: pip
+ path: .
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 0cf16e9..f62fdc1 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -4,17 +4,20 @@
[](https://pypi.org/project/deepbots/)
[](https://test.pypi.org/project/deepbots/)
+[](https://deepbots.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/deepbots)
[](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepbots/blob/dev/LICENSE)
[](#contributors-)
Deepbots is a simple framework which is used as "middleware" between the free
and open-source [Cyberbotics' Webots](https://cyberbotics.com/) robot simulator
-and Reinforcement Learning algorithms. When it comes to Reinforcement Learning
-the [OpenAI gym](https://gym.openai.com/) environment has been established as
-the most used interface between the actual application and the RL algorithm.
-Deepbots is a framework which follows the OpenAI gym environment interface
-logic in order to be used by Webots applications.
+and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms. When it comes to RL,
+[gym](https://www.gymlibrary.dev/) environments have been established
+as the most used interface between the actual application and the RL algorithm.
+
+**Deepbots is a framework which follows the gym interface logic and bridges the
+gap between the gym environment and the simulator to enable you to easily
+create custom RL environments in Webots.**
## Installation
@@ -28,7 +31,7 @@ logic in order to be used by Webots applications.
refer to
[Using Python](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-python#introduction)
to select the proper Python version for your system)
-3. Follow the [Using Python](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-python)
+3. Refer to the [Using Python](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-python)
guide provided by Webots
4. Webots provides a basic code editor, but if you want to use
[PyCharm](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/) as your IDE refer to
@@ -38,8 +41,10 @@ logic in order to be used by Webots applications.
You will probably also need a backend library to implement the neural networks,
such as [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) or
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/). Deepbots interfaces with RL agents
-using the OpenAI gym logic, so it can work with any backend library you choose
-to implement the agent with and any agent that already works with gym.
+using the gym logic, so it can work with any backend library you choose
+to implement the agent with and any agent that already works with gym, such
+as [stable-baselines3](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3)
+implementations.
### Install deepbots
@@ -48,6 +53,9 @@ Deepbots can be installed through the package installer
`pip install deepbots`
+If you encounter [this](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepbots/issues/143)
+issue please use `pip install setuptools==65.5.0` before installing deepbots.
+
## Official resources
- On
@@ -56,6 +64,8 @@ Deepbots can be installed through the package installer
- On [the deepworlds repository](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepworlds) you
can find examples of deepbots being used.
Feel free to contribute your
own!
+- On [the deepbots documentation site](https://deepbots.readthedocs.io/)
+ you can find the framework's documentation
## Citation
@@ -79,154 +89,6 @@ https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_6
```
-## How it works
-
-First of all let's set up a simple glossary:
-
-- `World`: Webots uses a tree structure to represent the different entities in
- the scene. The World is the root entity which contains all the
- entities/nodes. For example, the world contains the Supervisor and Robot
- entities as well as other objects which might be included in the scene.
-
-- `Supervisor`: The Supervisor is an entity which has access to all other
- entities of the world, while having no physical presence in it. For example,
- the Supervisor knows the exact position of all the entities of the world and
- can manipulate them. Additionally, the Supervisor has the Supervisor
- Controller as one of its child nodes.
-
-- `Supervisor Controller`: The Supervisor Controller is a python script which
- is responsible for the Supervisor. For example, in the Supervisor Controller
- script the distance between two entities in the world can be calculated.
-
-- `Robot`: The Robot is an entity that represents a robot in the world. It
- might have sensors and other active components, like motors, etc. as child
- entities. Also, one of its children is the Robot Controller. For example,
- [epuck](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/epuck) and
- [TIAGo](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/tiago-iron) are robots.
-
-- `Robot Controller`: The Robot Controller is a python script which is
- responsible for the Robot's movement and sensors. With the Robot Controller
- it is possible to observe the world and act accordingly.
-- `Environment`: The Environment is the interface as described by the OpenAI
- gym. The Environment interface has the following methods:
-
- - `get_observations()`: Return the observations of the robot. For example,
- metrics from sensors, a camera image etc.
-
- - step(action): Each timestep, the agent chooses an action, and the
- environment returns the observation, the reward and the state of the
- problem (done or not).
-
- - `get_reward(action)`: The reward the agent receives as a result of their
- action.
- - `is_done()`: Whether it’s time to reset the environment. Most (but not all)
- tasks are divided up into well-defined episodes, and done being True
- indicates the episode has terminated. For example, if a robot has the task
- to reach a goal, then the done condition might happen when the robot
- "touches" the goal.
- - `reset()`: Used to reset the world to the initial state.
-
-In order to set up a task in Deepbots it is necessary to understand the
-intention of the OpenAI gym environment. According to the OpenAI gym
-documentation, the framework follows the classic “agent-environment loop”.
-"Each timestep, the agent chooses an `action`, and the environment returns an
-`observation` and a `reward`. The process gets started by calling `reset()`,
-which returns an initial `observation`."
-
-
-  -
-
-
-Deepbots follows this exact agent-environment loop with the only difference
-being that the agent, which is responsible to choose an action, runs on the
-Supervisor and the observations are acquired by the robot. The goal of the
-deepbots framework is to hide this communication from the user, especially from
-those who are familiar with the OpenAI gym environment. More specifically,
-`SupervisorEnv` is the interface which is used by the Reinforcement Learning
-algorithms and follows the OpenAI Gym environment logic. The Deepbots framework
-provides different levels of abstraction according to the user's needs.
-Moreover, a goal of the framework is to provide different wrappers for a wide
-range of robots.
-
-Deepbots also provides a default implementation of the `reset()` method,
-leveraging Webots' built-in simulation reset functions, removing the need for
-the user to implement reset procedures for simpler use-cases. It is always
-possible to override this method and implement any custom reset procedure, as
-needed.
-
-#### Emitter - receiver scheme
-
-Currently, the communication between the `Supervisor` and the `Robot` is
-achieved via an `emitter` and a `receiver`. Separating the `Supervisor` from
-the `Robot`, deepbots can fit a variety of use-cases, e.g. multiple `Robots`
-collecting experience and a `Supervisor` controlling them with a single agent.
-The way Webots implements `emitter`/`receiver` communication requires messages
-to be packed and unpacked, which introduces an overhead that becomes
-prohibiting in use-cases where the observations are high-dimensional or long,
-such as camera images. Deepbots provides another partially abstract class that
-combines the `Supervisor` and the `Robot` into one controller and circumvents
-that issue, while being less flexible, which is discussed
-[later](#combined-robot-supervisor-scheme).
-
-
-  -
-
-
-On one hand, the `emitter` is an entity which is provided by Webots, that
-broadcasts messages to the world. On the other hand, the `receiver` is an
-entity that is used to receive messages from the `World`. Consequently, the
-agent-environment loop is transformed accordingly. Firstly, the `Robot` uses
-its sensors to retrieve the observation from the `World` and in turn uses the
-`emitter` component to broadcast this observation. Secondly, the `Supervisor`
-receives the observation via the `receiver` component and in turn, the agent
-uses it to choose an action. It should be noted that the observation the agent
-uses might be extended from the `Supervisor`. For example, a model might use
-LiDAR sensors installed on the `Robot`, but also the Euclidean distance between
-the `Robot` and an object. As it is expected, the `Robot` does not know the
-Euclidean distance, only the `Supervisor` can calculate it, because it has
-access to all entities in the `World`.
-
-You can follow the
-[emitter-receiver scheme tutorial](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-tutorials/blob/master/emitterReceiverSchemeTutorial/README.md)
-to get started and work your way up from there.
-
-
-  -
-
-
-#### Combined Robot-Supervisor scheme
-
-As mentioned earlier, in use-cases where the observation transmitted between
-the `Robot` and the `Supervisor` is high-dimensional or long, e.g. high
-resolution images taken from a camera, a significant overhead is introduced.
-This is circumvented by inheriting and implementing the partially abstract
-`RobotSupervisor` that combines the `Robot controller` and the
-`Supervisor Controller` into one, forgoing all `emitter`/`receiver`
-communication. This new controller runs on the `Robot`, but requires
-`Supervisor` privileges and is limited to one `Robot`, one `Supervisor`.
-
-You can follow the
-[robot-supervisor scheme tutorial](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-tutorials/tree/master/robotSupervisorSchemeTutorial)
-to get started and work your way up from there. We recommended this
-tutorial to get started with deepbots.
-
-### Abstraction Levels
-
-The deepbots framework has been created mostly for educational purposes. The
-aim of the framework is to enable people to use Reinforcement Learning in
-Webots. More specifically, we can consider deepbots as a wrapper of Webots
-exposing an OpenAI gym style interface. For this reason there are multiple
-levels of abstraction. For example, a user can choose if they want to use CSV
-`emitter`/`receiver` or if they want to make an implementation from scratch. In
-the top level of the abstraction hierarchy is the `SupervisorEnv` which is the
-OpenAI gym interface. Below that level there are partially implemented classes
-with common functionality. These implementations aim to hide the communication
-between the `Supervisor` and the `Robot`, as described in the two different
-schemes ealier. Similarly, in the `emitter`/`receiver` scheme the `Robot` also
-has different abstraction levels. According to their needs, users can choose
-either to process the messages received from the `Supervisor` themselves or use
-the existing implementations.
-
### Acknowledgments
This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020
diff --git a/deepbots/supervisor/controllers/deepbots_supervisor_env.py b/deepbots/supervisor/controllers/deepbots_supervisor_env.py
index d2da665..e012816 100644
--- a/deepbots/supervisor/controllers/deepbots_supervisor_env.py
+++ b/deepbots/supervisor/controllers/deepbots_supervisor_env.py
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ def reset(self):
Default, problem-agnostic, implementation of reset method,
using Webots-provided methods.
- *Note that this works properly only with Webots versions >R2020b
+ \*Note that this works properly only with Webots versions >R2020b
and must be overridden with a custom reset method when using
earlier versions. It is backwards compatible due to the fact
that the new reset method gets overridden by whatever the user
diff --git a/docs/Makefile b/docs/Makefile
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d4bb2cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/Makefile
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+# Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
+#
+
+# You can set these variables from the command line, and also
+# from the environment for the first two.
+SPHINXOPTS ?=
+SPHINXBUILD ?= sphinx-build
+SOURCEDIR = .
+BUILDDIR = _build
+
+# Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
+help:
+ @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
+
+.PHONY: help Makefile
+
+# Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
+# "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
+%: Makefile
+ @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
diff --git a/docs/_static/css/baselines_theme.css b/docs/_static/css/baselines_theme.css
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1ce4997
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/_static/css/baselines_theme.css
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+/* Taken from https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3/blob/master/docs/_static/css/baselines_theme.css */
+
+/* Main colors adapted from pytorch doc */
+:root{
+ --main-bg-color: #343A40;
+ --link-color: #FD7E14;
+}
+
+/* Header fonts y */
+h1, h2, .rst-content .toctree-wrapper p.caption, h3, h4, h5, h6, legend, p.caption {
+ font-family: "Lato","proxima-nova","Helvetica Neue",Arial,sans-serif;
+}
+
+
+/* Docs background */
+.wy-side-nav-search{
+ background-color: var(--main-bg-color);
+}
+
+/* Mobile version */
+.wy-nav-top{
+ background-color: var(--main-bg-color);
+}
+
+/* Change link colors (except for the menu) */
+a {
+ color: var(--link-color);
+}
+
+a:hover {
+ color: #4F778F;
+}
+
+.wy-menu a {
+ color: #b3b3b3;
+}
+
+.wy-menu a:hover {
+ color: #b3b3b3;
+}
+
+a.icon.icon-home {
+ color: #b3b3b3;
+}
+
+.version{
+ color: var(--link-color) !important;
+}
+
+
+/* Make code blocks have a background */
+.codeblock,pre.literal-block,.rst-content .literal-block,.rst-content pre.literal-block,div[class^='highlight'] {
+ background: #f8f8f8;;
+}
+
+/* Change style of types in the docstrings .rst-content .field-list */
+.field-list .xref.py.docutils, .field-list code.docutils, .field-list .docutils.literal.notranslate
+{
+ border: None;
+ padding-left: 0;
+ padding-right: 0;
+ color: #404040;
+}
diff --git a/doc/img/agent_env_loop.svg b/docs/_static/img/agent_env_loop.svg
similarity index 100%
rename from doc/img/agent_env_loop.svg
rename to docs/_static/img/agent_env_loop.svg
diff --git a/doc/img/deepbots_overview.png b/docs/_static/img/deepbots_overview.png
similarity index 100%
rename from doc/img/deepbots_overview.png
rename to docs/_static/img/deepbots_overview.png
diff --git a/doc/img/workflow_diagram.png b/docs/_static/img/workflow_diagram.png
similarity index 100%
rename from doc/img/workflow_diagram.png
rename to docs/_static/img/workflow_diagram.png
diff --git a/docs/conf.py b/docs/conf.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e014622
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/conf.py
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+# Configuration file for the Sphinx documentation builder.
+#
+# This file only contains a selection of the most common options. For a full
+# list see the documentation:
+# https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html
+
+# -- Path setup --------------------------------------------------------------
+
+# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
+# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
+# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
+#
+import os
+import sys
+
+sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('../'))
+sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('../deepbots/'))
+sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('.'))
+
+# -- Project information -----------------------------------------------------
+
+project = "deepbots"
+copyright = "GNU General Public License v3.0"
+author = "aidudezzz"
+
+# -- General configuration ---------------------------------------------------
+# -- General configuration
+
+extensions = [
+ "sphinx.ext.duration",
+ "sphinx.ext.doctest",
+ "sphinx.ext.autodoc",
+ "sphinx.ext.autosummary",
+ 'sphinx.ext.viewcode',
+ "sphinx.ext.intersphinx",
+ "sphinx_copybutton"
+]
+
+intersphinx_mapping = {
+ "rtd": ("https://docs.readthedocs.io/en/stable/", None),
+ "python": ("https://docs.python.org/3/", None),
+ "sphinx": ("https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/", None),
+}
+intersphinx_disabled_domains = ["std"]
+
+templates_path = ["_templates"]
+
+# -- Options for EPUB output
+epub_show_urls = "footnote"
+
+# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
+# directories to ignore when looking for source files.
+# This pattern also affects html_static_path and html_extra_path.
+exclude_patterns = ["_build", "Thumbs.db", ".DS_Store"]
+
+# This is needed to ignore the webots imports "from controller..."
+autodoc_mock_imports = ["controller"]
+
+# Order class methods on how they appear in the source code
+autodoc_member_order = "bysource"
+
+
+# -- Options for HTML output -------------------------------------------------
+
+def setup(app):
+ app.add_css_file("css/baselines_theme.css")
+
+
+# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
+# a list of builtin themes.
+#
+html_theme = "sphinx_rtd_theme"
+
+# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
+# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
+# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
+html_static_path = ["_static"]
+
+html_logo = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-swag/main/logo/deepbots_square_smaller.png'
+html_favicon = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-swag/main/logo/favicon.ico'
diff --git a/docs/deepbots/deepbots.robots.controllers.rst b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.robots.controllers.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..da2caee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.robots.controllers.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+deepbots.robots.controllers
+===========================
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.robots.EmitterReceiverRobot
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.robots.CSVRobot
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. automodule:: deepbots.robots.controllers
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/deepbots/deepbots.rst b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8bdbd0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+deepbots
+=========
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 2
+
+ deepbots.robots.controllers
+ deepbots.supervisor
+
+.. automodule:: deepbots
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.controllers.rst b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.controllers.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..30ecfd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.controllers.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+deepbots.supervisor.controllers
+===============================
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.DeepbotsSupervisorEnv
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.RobotSupervisorEnv
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.EmitterReceiverSupervisorEnv
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.CSVSupervisorEnv
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. automodule:: deepbots.supervisor.controllers
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.rst b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..de75bc4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+deepbots.supervisor
+===================
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 2
+
+ deepbots.supervisor.controllers
+ deepbots.supervisor.wrappers
+
+.. automodule:: deepbots.supervisor
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.wrappers.rst b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.wrappers.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..38001df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/deepbots/deepbots.supervisor.wrappers.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+deepbots.supervisor.wrappers
+============================
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.wrappers.keyboard_printer.KeyboardPrinter
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. autoclass:: deepbots.supervisor.wrappers.tensorboard_wrapper.TensorboardLogger
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
+
+.. automodule:: deepbots.supervisor.wrappers
+ :members:
+ :undoc-members:
+ :show-inheritance:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/how_deepbots_works.rst b/docs/how_deepbots_works.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..55e711b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/how_deepbots_works.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
+How *deepbots* works
+====================
+
+Here you can find a high-level explanation on how the framework is structured
+and how it actually works.
+
+**Read on if you want to dig deeper into how and why
+deepbots works the way it does. If you want a quick start, visit our**
+`beginner tutorial `_
+and if you want to see *deepbots* in action, visit `deepworlds `_!
+
+Overview
+--------
+
+First of all let's set up a simple glossary:
+
+* `World`: Webots uses a tree structure to represent the different entities in
+ the scene. The World is the root entity which contains all the
+ Webots entities/nodes. For example, the world contains the Supervisor and
+ Robot entities as well as other objects which might be included in the scene.
+
+* `Supervisor`: The Supervisor is an entity which has access to all other
+ entities of the world, which can have a physical presence or not. For
+ example, the Supervisor knows the exact position of all the entities of the
+ world and can manipulate them.
+
+* `Supervisor Controller`: The Supervisor Controller is a python script which
+ is responsible for the Supervisor. For example, in the Supervisor Controller
+ script the distance between two entities in the world can be calculated or
+ entities can be moved around, etc.
+
+* `Robot`: The Robot is an entity that represents a robot in the world. It
+ might have sensors and other active components, like motors, etc., as child
+ entities. For example, `epuck `_ and
+ `TIAGo `_ are robots.
+
+* `Robot Controller`: The Robot Controller is a python script which is
+ responsible for the Robot's movement and sensors. With the Robot Controller
+ it is possible to observe the world and act accordingly by for example
+ turning the Robot's motors.
+
+* `Environment`: The Environment is the interface as described by
+ The Environment must have the following methods:
+
+ * `get_observations()`: Return the observations of the robot. For example,
+ metrics from sensors, a camera image, etc.
+
+ * `step(action)`: In each timestep, the agent chooses an action and the
+ environment returns the observation, the reward and the state of the
+ problem (done or not).
+
+ * `get_reward(action)`: The reward the agent receives as a result of their
+ action, based on which it gets trained.
+
+ * `is_done()`: Whether it’s time to reset the environment. Most (but not all)
+ tasks are divided up into well-defined episodes, and done being True
+ indicates the episode has terminated. For example, if a robot has
+ to reach a goal, then the done condition might happen when the robot
+ "touches" the goal, or when it collides with an obstacle.
+
+ * `reset()`: Used to reset the world to the initial state and start a new
+ training episode.
+
+
+In order to set up a task in *deepbots* it is necessary to understand the
+intention of the gym environment. According to gym's
+documentation, the framework follows the classic “agent-environment loop”.
+"Each timestep, the agent chooses an `action`, and the environment returns an
+`observation` and a `reward`. The process gets started by calling `reset()`,
+which returns an initial `observation`."
+
+.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots/dev/doc/img/agent_env_loop.svg
+ :alt: Agent-environment loop
+ :align: center
+
+*Deepbots* follows this exact agent-environment loop with the only difference
+being that the agent, which is responsible to choose an action, runs on the
+`Supervisor` and the observations are acquired by the `Robot`. The goal of
+*deepbots* is to bridge the gap between the gym environment and the Webots
+robot simulator. More specifically,
+:py:meth:`deepbots.supervisor.DeepbotsSupervisorEnv` is the main class that
+provides the interface which is used by the Reinforcement Learning algorithms
+and follows gym's environment logic. *Deepbots* provides different levels of
+abstraction to be used according to the user's needs. Moreover, the framework
+provides different wrappers for additional functionalities.
+
+*Deepbots* also provides a default implementation of the `reset()` method,
+leveraging Webots' built-in simulation reset functions, removing the need for
+the user to implement reset procedures for simpler use-cases. It is always
+possible to override this method and implement any custom reset procedure as
+needed by the use-case.
+
+**All-in-all to set up your gym environment you have to create a class that
+inherits one of deepbots' classes and implement the methods that are specific
+to your use-case and deepbots will handle interfacing the environment with
+Webots. As your familiarity and/or needs grow, you can override deepbots'
+methods to alter functionality or inherit from classes higher up in the
+hierarchy.**
+
+*Deepbots* targets users that are unfamiliar with either Webots or
+gym environments or both. If you have a strong understanding of both, you can
+forgo using *deepbots* altogether, but if you chose otherwise, it can make
+your code more modular and clean.
+
+The two *deepbots* schemes
+--------------------------
+
+*Deepbots* includes two schemes to set up your RL environment, the
+`emitter-receiver scheme` which separates the `Robot` and the `Supervisor` in
+two different entities and the `Robot-Supevisor scheme` which combines them
+into one entity. Both are described below.
+
+Emitter - receiver scheme
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+In this scheme the `Robot` and the `Supervisor` are separated into two entities
+within the World. Communication between the two nodes is needed so the
+`Supervisor` can send the agent's actions to the `Robot` and for the `Robot`
+to send back its observations, and can be achieved in various ways.
+The main way communication between the `Supervisor` and the `Robot` is
+achieved, is via `emitters` and `receivers`. By separating the `Supervisor`
+from the `Robot`, *deepbots* can fit a variety of use-cases, e.g. multiple
+`Robots` collecting experience and a `Supervisor` controlling them with a
+single agent. The way Webots implements `emitter`/`receiver` communication
+requires messages to be packed and unpacked, which introduces an overhead that
+becomes prohibiting in use-cases where the observations are high-dimensional
+or long, such as camera images. *Deepbots* provides another scheme that
+combines the `Supervisor` and the `Robot` into one controller and circumvents
+that issue, while being less flexible, which is discussed
+:ref:`later `.
+
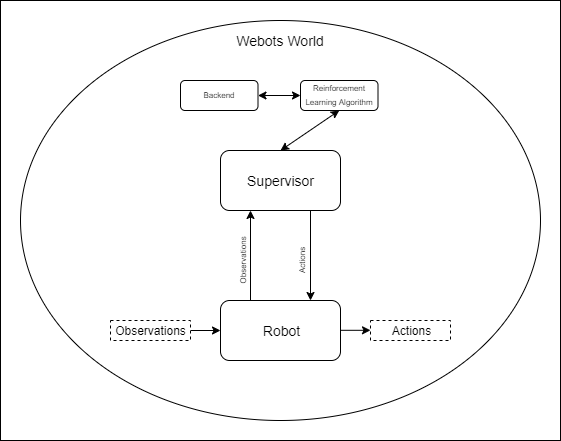
+.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots/dev/doc/img/deepbots_overview.png
+ :alt: Deepbots overview
+ :align: center
+
+On one hand, the `emitter` is an entity which is provided by Webots, that
+broadcasts messages to the world. On the other hand, the `receiver` is an
+entity that is used to receive messages from the `World`. Consequently, the
+agent-environment loop is transformed accordingly. Firstly, the `Robot` uses
+its sensors to retrieve the observation from the `World` and in turn uses its
+`emitter` component to broadcast it. Secondly, the `Supervisor`
+receives the observation via its `receiver` component and in turn, the agent
+uses it to choose an action. The `Supervisor` uses its `emitter` to broadcast
+the action, which the `Robot` receives with its `receiver`, closing the loop.
+
+It should be noted that the observation the agent
+uses might be extended in the `Supervisor` with additional values that the
+`Robot` might not have access to. For example, an observation might include
+LiDAR sensors values taken from the `Robot`, but also the Euclidean distance
+between the `Robot` and an object. As expected, the `Robot` cannot calculate
+the Euclidean distance, but the `Supervisor` can, because it has access to all
+entities in the `World` and their positions.
+
+You can take a look at the `Supervisor` and `Robot` classes implementations for
+this scheme in :py:meth:`deepbots.supervisor.EmitterReceiverSupervisorEnv`/
+:py:meth:`deepbots.supervisor.CSVSupervisorEnv` and
+:py:meth:`deepbots.robots.EmitterReceiverRobot`/:py:meth:`deepbots.robots.CSVRobot`
+respectively.
+
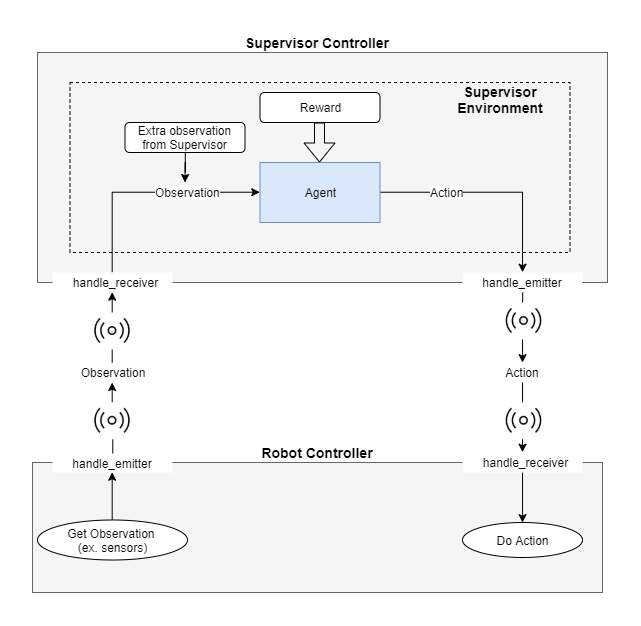
+You can follow the
+`emitter-receiver scheme tutorial `_
+to get started and work your way up from there.
+
+.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots/dev/doc/img/workflow_diagram.png
+ :alt: Workflow diagram
+ :align: center
+
+.. _combined:
+
+Combined Robot-Supervisor scheme
+^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
+
+As mentioned earlier, in use-cases where the observation transmitted between
+the `Robot` and the `Supervisor` is high-dimensional or long, e.g. high
+resolution images taken from a camera, a significant overhead is introduced.
+This is circumvented by inheriting and implementing the partially abstract
+`RobotSupervisorEnv` that combines the `Robot Controller` and the
+`Supervisor Controller` into one, forgoing all `emitter`/`receiver`
+communication. This controller runs on the `Robot`, but requires
+`Supervisor` privileges and is limited to one `Robot` - one `Supervisor`.
+
+You can take a look at the combined `Robot - Supervisor` environment class in
+:py:meth:`deepbots.supervisor.RobotSupervisorEnv`, which acts both as the
+`Robot Controller`/`Supervisor Controller` and the `Environment` the RL agent
+interacts with.
+
+You can follow the
+`robot-supervisor scheme tutorial `_
+to get started and work your way up from there. **We recommend this
+scheme/tutorial to get started with deepbots.**
+
+Abstraction Levels
+------------------
+
+The *deepbots* framework has been created mostly for educational and
+research purposes. The aim of the framework is to enable people to use
+Reinforcement Learning in Webots. More specifically, we can consider *deepbots*
+as a wrapper of Webots exposing a gym-style interface. For this reason there
+are multiple levels of abstraction via a family of classes. For example, a user
+can choose if they want to use a CSV `emitter`/`receiver` or if they want to
+make a communication implementation from scratch. In the top level of the
+abstraction hierarchy is the `DeepbotsSupervisorEnv` class which is the main
+gym interface. Below that level there are partially implemented classes
+with common functionality. These implementations aim to hide the communication
+between the `Supervisor` and the `Robot` and other various functions needed by
+the simulator for a gym environment to work, as described in the two different
+schemes earlier. Feel free to explore the documentation and the full family
+of classes and to create and customize your own, inheriting from whichever
+*deepbots* class you choose according to your needs.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/index.rst b/docs/index.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..45887c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/index.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+**Deepbots** framework docs - Reinforcement Learning in Webots
+==============================================================
+
+.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-swag/main/logo/deepbots_full.png
+ :alt: Deepbots logo
+
+.. note::
+
+ The documentation site is under active development. Check out `this PR `_
+ for an idea on what to expect in the future!
+
+`Deepbots `_ is a simple framework
+which is used as "middleware" between the free and open-source
+`Cyberbotics' Webots `_ robot simulator
+and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms. When it comes to RL,
+`gym `_ environments have been established
+as the most used interface between the actual application and the RL algorithm.
+
+**Deepbots is a framework which follows the gym interface logic and bridges the
+gap between the gym environment and the simulator to enable you to easily
+create custom RL environments in Webots.**
+
+Contents
+--------
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 2
+ :caption: General
+
+ Home
+ installation
+ how_deepbots_works
+
+.. toctree::
+ :maxdepth: 2
+ :caption: Reference
+
+ deepbots/deepbots
+
+Official resources
+------------------
+
+- On
+ `the deepbots-tutorials repository `_
+ you can find the official tutorials for deepbots
+- On `the deepworlds repository `_ you
+ can find examples of deepbots being used.
Feel free to contribute your
+ own!
+
+Citation
+________
+
+Conference paper (AIAI2020):
+https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_6
+
+.. code-block:: bibtex
+
+ @InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_6,
+ author="Kirtas, M.
+ and Tsampazis, K.
+ and Passalis, N.
+ and Tefas, A.",
+ title="Deepbots: A Webots-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Robotics",
+ booktitle="Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations",
+ year="2020",
+ publisher="Springer International Publishing",
+ address="Cham",
+ pages="64--75",
+ isbn="978-3-030-49186-4"
+ }
+
+Acknowledgments
+---------------
+
+This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020
+research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 871449 (OpenDR).
+This publication reflects the authors’ views only. The European Commission is
+not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains.
+
+Indices
+-------
+
+* :ref:`genindex`
+* :ref:`modindex`
diff --git a/docs/installation.rst b/docs/installation.rst
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7cfc42c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/installation.rst
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+Installation
+============
+
+.. note::
+
+ It's probably a safer choice to install deepbots in a virtual environment.
+ You can do that using `venv `_:
+
+ ``python3 -m venv deepbots-env``
+
+ and then activate it:
+
+ ``source deepbots-env/bin/activate``
+
+ before installing `deepbots` and other python prerequisites such as the
+ backend neural network framework.
+
+Prerequisites
+-------------
+
+#. `Install Webots `_
+
+ * `Windows `_
+ * `Linux `_
+ * `macOS `_
+
+#. `Install Python version 3.X `_ (please refer to
+ `Using Python `__
+ to select the proper Python version for your system)
+#. Refer to the `Using Python `__
+ guide provided by Webots
+#. Webots provides a basic code editor, but if you want to use
+ `PyCharm `_ as your IDE refer to
+ `using PyCharm IDE `_
+ provided by Webots
+
+You will probably also need a backend library to implement the neural networks,
+such as `PyTorch `_ or
+`TensorFlow `_. Deepbots interfaces with RL agents
+using the gym logic, so it can work with any backend library you choose
+to implement the agent with and any agent that already works with gym, such
+as `stable-baselines3 `_
+implementations.
+
+Install deepbots
+----------------
+
+Deepbots can be installed through the package installer
+`pip `_ running the following command:
+
+.. code-block:: bash
+
+ pip install deepbots
+
+.. note::
+
+ If you encounter `the extras_require issue `_
+ please try :code:`pip install setuptools==65.5.0` before installing deepbots.
+
+.. role:: bash(code)
+ :language: bash
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/make.bat b/docs/make.bat
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..954237b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/make.bat
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+@ECHO OFF
+
+pushd %~dp0
+
+REM Command file for Sphinx documentation
+
+if "%SPHINXBUILD%" == "" (
+ set SPHINXBUILD=sphinx-build
+)
+set SOURCEDIR=.
+set BUILDDIR=_build
+
+%SPHINXBUILD% >NUL 2>NUL
+if errorlevel 9009 (
+ echo.
+ echo.The 'sphinx-build' command was not found. Make sure you have Sphinx
+ echo.installed, then set the SPHINXBUILD environment variable to point
+ echo.to the full path of the 'sphinx-build' executable. Alternatively you
+ echo.may add the Sphinx directory to PATH.
+ echo.
+ echo.If you don't have Sphinx installed, grab it from
+ echo.https://www.sphinx-doc.org/
+ exit /b 1
+)
+
+if "%1" == "" goto help
+
+%SPHINXBUILD% -M %1 %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
+goto end
+
+:help
+%SPHINXBUILD% -M help %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
+
+:end
+popd
diff --git a/docs/requirements.in b/docs/requirements.in
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..acbc25d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/requirements.in
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+Sphinx>=5,<6
+sphinx_rtd_theme
diff --git a/docs/requirements.txt b/docs/requirements.txt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..293b012
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/requirements.txt
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+#
+# This file is autogenerated by pip-compile with python 3.10
+# To update, run:
+#
+# pip-compile docs/requirements.in
+#
+alabaster==0.7.12
+ # via sphinx
+babel==2.10.3
+ # via sphinx
+certifi==2022.6.15
+ # via requests
+charset-normalizer==2.1.0
+ # via requests
+docutils==0.17.1
+ # via
+ # sphinx
+ # sphinx-rtd-theme
+idna==3.3
+ # via requests
+imagesize==1.4.1
+ # via sphinx
+jinja2==3.1.2
+ # via sphinx
+markupsafe==2.1.1
+ # via jinja2
+packaging==21.3
+ # via sphinx
+pygments==2.12.0
+ # via sphinx
+pyparsing==3.0.9
+ # via packaging
+pytz==2022.1
+ # via babel
+requests==2.28.1
+ # via sphinx
+snowballstemmer==2.2.0
+ # via sphinx
+sphinx==5.0.2
+ # via
+ # -r docs/requirements.in
+ # sphinx-rtd-theme
+sphinx-rtd-theme==1.0.0
+ # via -r docs/requirements.in
+sphinxcontrib-applehelp==1.0.2
+ # via sphinx
+sphinxcontrib-devhelp==1.0.2
+ # via sphinx
+sphinxcontrib-htmlhelp==2.0.0
+ # via sphinx
+sphinxcontrib-jsmath==1.0.1
+ # via sphinx
+sphinxcontrib-qthelp==1.0.3
+ # via sphinx
+sphinxcontrib-serializinghtml==1.1.5
+ # via sphinx
+urllib3==1.26.9
+ # via requests
+setuptools==65.5.0
+sphinx_copybutton
+
diff --git a/pyproject.toml b/pyproject.toml
index 2beee6a..fd0bfad 100644
--- a/pyproject.toml
+++ b/pyproject.toml
@@ -2,6 +2,10 @@
requires = ["setuptools==65.5.0", "wheel"]
build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
+[project]
+name = "deepbots"
+authors = [{name = "aidudezzz", email = "deepbots@protonmail.com"}]
+dynamic = ["version", "description"]
[tool.black]
line-length = 79
 -
-
 -
- -
-